Food Insecurity and Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Severity
- PMID: 37931698
- PMCID: PMC11108653
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2023.113818
Food Insecurity and Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Severity
Abstract
Objective: To determine the association between food insecurity and pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Methods: Cross-sectional study of patients < 21 years of age with histologically confirmed NAFLD. The Household Food Security Survey Module was administered to determine food insecurity status. Skin lipidomics were performed to explore pathophysiologic mechanisms.
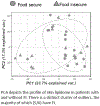
Results: Seventy-three patients with histologically confirmed NAFLD completed the Household Food Security Survey Module. Of these, the majority were male (81%) and non-Hispanic (53%), with a mean age at biopsy of 13 ± 3 years. Food insecurity was seen in 42% (n = 31). Comparison of features between food insecure and food secure subgroups revealed no differences in sex, ethnicity, BMI z-score, aminotransferases, or histologic severity. However, children experiencing food insecurity presented on average 2 years before their food secure counterparts (12.3 ± 3.0 vs 14.4 ± 3.6 years, P = .015). A subset of 31 patients provided skin samples. Skin lipidomics revealed that food insecurity was associated with down-regulated features from the lipoamino acid class of lipids, previously linked to inflammation and adipocyte differentiation.
Conclusions: Food insecurity is highly prevalent in children with NAFLD and is associated with earlier presentation. Lipidomic analyses suggest a possible pathophysiologic link that warrants further exploration.
Keywords: NAFLD; cutaneous biomarker; fatty liver; food security; lipidomics.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest SO was funded by the NASPGHAN Foundation/ Abbott Nutrition Advanced Fellowship Training in Pediatric Nutrition (2019) and the NIHP30 DK078392 of the Digestive Diseases Research Core Center in Cincinnati. The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Doycheva I, Issa D, Watt KD, Lopez R, Rifai G, Alkhouri N. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the most rapidly increasing indication for liver transplantation in young adults in the United States. J Clin Gastroenterol 2018;52:339–46. - PubMed
-
- Zelber-Sagi S, Ivancovsky-Wajcman D, Fliss Isakov N, Webb M, Orenstein D, Shibolet O, et al. High red and processed meat consumption is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. J Hepatol 2018;68:1239–46. - PubMed
-
- Leon-Plascencia AL M, Larrosa-Haro A, Romero-Velarde E, Bravo-Nunez EC, López-Marure E. Dietary and sociodemographic factors associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese pediatric patients. Rev Gastroenterol Mex (Engl Ed) 2021;86:236–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

