Real-World Compliance of Surgical Treatment According to the Korean Gastric Cancer Guideline 2018: Evaluation From the Nationwide Survey Data 2019 in Korea
- PMID: 37932221
- PMCID: PMC10630559
- DOI: 10.5230/jgc.2023.23.e32
Real-World Compliance of Surgical Treatment According to the Korean Gastric Cancer Guideline 2018: Evaluation From the Nationwide Survey Data 2019 in Korea
Abstract
Purpose: This study evaluated real-world compliance with surgical treatment according to Korea's gastric cancer treatment guidelines.
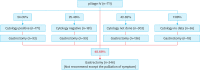
Materials and methods: The 2018 Korean Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines were evaluated using the 2019 national survey data for surgically treated gastric cancer based on postoperative pathological results in Korea. In addition, the changes in surgical treatments in 2019 were compared with those in the 2014 national survey data implemented before the publication of the guidelines in 2018. The compliance rate was evaluated according to the algorithm recommended in the 2018 Korean guidelines.
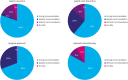
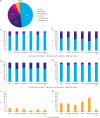
Results: The overall compliance rates in 2019 were 83% for gastric resection extent, 87% for lymph node dissection, 100% for surgical approach, and 83% for adjuvant chemotherapy, similar to 2014. Among patients with pathologic stages IB, II, and III disease who underwent total gastrectomy, the incidence of splenectomy was 8.08%, a practice not recommended by the guidelines. The survey findings revealed that 48.66% of the patients who underwent gastrectomy had pathological stage IV disease, which was not recommended by the 2019 guidelines. Compared to that in 2014, the rate of gastrectomy in stage IV patients was 54.53% in 2014. Compliance rates were similar across all regions of Korea, except for gastrectomy in patients with stage IV disease.
Conclusions: Real-world compliance with gastric cancer treatment guidelines was relatively high in Korea.
Keywords: Compliance; Guideline; Stomach neoplasm.
Copyright © 2023. Korean Gastric Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures






References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Worhunsky DJ, Ma Y, Zak Y, Poultsides GA, Norton JA, Rhoads KF, et al. Compliance with gastric cancer guidelines is associated with improved outcomes. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2015;13:319–325. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

