Radiomics-based decision support tool assists radiologists in small lung nodule classification and improves lung cancer early diagnosis
- PMID: 37932513
- PMCID: PMC10703918
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-023-02480-y
Radiomics-based decision support tool assists radiologists in small lung nodule classification and improves lung cancer early diagnosis
Abstract
Background: Methods to improve stratification of small (≤15 mm) lung nodules are needed. We aimed to develop a radiomics model to assist lung cancer diagnosis.
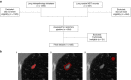
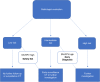
Methods: Patients were retrospectively identified using health records from January 2007 to December 2018. The external test set was obtained from the national LIBRA study and a prospective Lung Cancer Screening programme. Radiomics features were extracted from multi-region CT segmentations using TexLab2.0. LASSO regression generated the 5-feature small nodule radiomics-predictive-vector (SN-RPV). K-means clustering was used to split patients into risk groups according to SN-RPV. Model performance was compared to 6 thoracic radiologists. SN-RPV and radiologist risk groups were combined to generate "Safety-Net" and "Early Diagnosis" decision-support tools.
Results: In total, 810 patients with 990 nodules were included. The AUC for malignancy prediction was 0.85 (95% CI: 0.82-0.87), 0.78 (95% CI: 0.70-0.85) and 0.78 (95% CI: 0.59-0.92) for the training, test and external test datasets, respectively. The test set accuracy was 73% (95% CI: 65-81%) and resulted in 66.67% improvements in potentially missed [8/12] or delayed [6/9] cancers, compared to the radiologist with performance closest to the mean of six readers.
Conclusions: SN-RPV may provide net-benefit in terms of earlier cancer diagnosis.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Professor Devaraj reports personal fees from Brainomix, Roche, and Boehringer Ingelheim and has stock options in Brainomix. Dr Lee is funded by the Royal Marsden NIHR BRC, Royal Marsden Cancer Charity and SBRI (including QURE.AI). RL’s institution receives compensation for time spent in a secondment role for the lung health check programme and as a National Specialty Lead for the National Institute of Health and Care Research. He has received research funding from CRUK, Innovate UK (co-funded by GE Healthcare, Roche and Optellum), SBRI, RM Partners Cancer Alliance and NIHR (co-applicant in grants with Optellum). He has received honoraria from CRUK. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lam S, Bryant H, Donahoe L, Domingo A, Earle C, Finley C, et al. Management of screen-detected lung nodules: a Canadian partnership against cancer guidance document. Can J Respir Crit Care Sleep Med. 2020;4:236–65.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

