The diagnostic performance of AFP and PIVKA-II models for non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37932802
- PMCID: PMC10629103
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-023-06600-y
The diagnostic performance of AFP and PIVKA-II models for non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to describe the diagnostic performance of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), alpha-fetoprotein L3 isoform (AFP-L3), protein induced by vitamin K absence II (PIVKA-II), and combined biomarkers for non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma (NBNC-HCC).
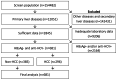
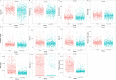
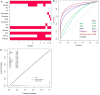
Results: A total of 681 newly-diagnosed primary liver disease subjects (385 non-HCC, 296 HCC) who tested negativity for the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and hepatitis C antibody (anti-HCV) enrolled in this study. At the cut-off point of 3.8 ng/mL, AFP helps to discriminate HCC from non-HCC with an area under the curve (AUC) value of 0.817 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.785-0.849). These values of AFP-L3 (cut-off 0.9%) and PIVKA-II (cut-off 57.7 mAU/mL) were 0.758 (95%CI: 0.725-0.791) and 0.866 (95%CI: 0.836-0.896), respectively. The Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA) statistic identified the optimal model, including patients' age, aspartate aminotransferase, AFP, and PIVKA-II combination, which helps to classify HCC with better performance (AUC = 0.896, 95%CI: 0.872-0.920, P < 0.001). The sensitivity and specificity of the optimal model reached 81.1% (95%CI: 76.1-85.4) and 83.2% (95%CI: 78.9-86.9), respectively. Further analyses indicated that AFP and PIVKA-II markers and combined models have good-to-excellent performance detecting curative resected HCC, separating HCC from chronic hepatitis, dysplastic, and hyperplasia nodules.
Keywords: AFP; AFP-L3; Diagnosis; NBNC-HCC; PIVKA-II.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Fan J, Chen Y, Zhang D, Yao J, Zhao Z, Jiang Y, et al. Evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin and alpha-fetoprotein alone or in combination for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Oncol. 2020;34:245–55. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2020.05.002. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

