Clinical importance of changes in magnetic resonance biomarkers for Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 37932907
- PMCID: PMC10791017
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51933
Clinical importance of changes in magnetic resonance biomarkers for Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
Objective: Magnetic resonance (MR) measures of muscle quality are highly sensitive to disease progression and predictive of meaningful functional milestones in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). This investigation aimed to establish the reproducibility, responsiveness to disease progression, and minimum clinically important difference (MCID) for multiple MR biomarkers at different disease stages in DMD using a large natural history dataset.
Methods: Longitudinal MR imaging and spectroscopy outcomes and ambulatory function were measured in 180 individuals with DMD at three sites, including repeated measurements on two separate days (within 1 week) in 111 participants. These data were used to calculate day-to-day reproducibility, responsiveness (standardized response mean, SRM), minimum detectable change, and MCID. A survey of experts was also performed.
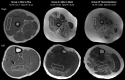
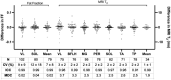
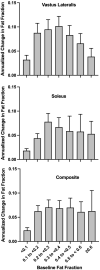
Results: MR spectroscopy fat fraction (FF), as well as MR imaging transverse relaxation time (MRI-T2 ), measures performed in multiple leg muscles, and had high reproducibility (Pearson's R > 0.95). Responsiveness to disease progression varied by disease stage across muscles. The average FF from upper and lower leg muscles was highly responsive (SRM > 0.9) in both ambulatory and nonambulatory individuals. MCID estimated from the distribution of scores, by anchoring to function, and via expert opinion was between 0.01 and 0.05 for FF and between 0.8 and 3.7 ms for MRI-T2 .
Interpretation: MR measures of FF and MRI T2 are reliable and highly responsive to disease progression. The MCID for MR measures is less than or equal to the typical annualized change. These results confirm the suitability of these measures for use in DMD and potentially other muscular dystrophies.
© 2023 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not report any conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to this study.
Figures

References
-
- Verhaart IEC, Aartsma‐Rus A. Therapeutic developments for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(7):373‐386. - PubMed
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services F, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research . Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Related Dystrophinopathies: Developing Drugs for Treatment Guidance for Industry. 2018.
-
- Finkel RS, Finanger E, Vandenborne K, et al. Disease‐modifying effects of edasalonexent, an NF‐kappaB inhibitor, in young boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: results of the MoveDMD phase 2 and open label extension trial. Neuromuscul Disord. 2021;31(5):385‐396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
