A modern approach with follower-leading clustering algorithm for visualizing author collaborations and article themes in skin cancer research: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 37933006
- PMCID: PMC10627629
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034801
A modern approach with follower-leading clustering algorithm for visualizing author collaborations and article themes in skin cancer research: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Skin cancers (SCs) arise due to the proliferation of atypical cells that have the potential to infiltrate or metastasize to different areas of the body. There is a lack of understanding regarding the country-based collaborations among authors (CBCA) and article themes on SCs. A clustering algorithm capable of categorizing CBCA and article themes on skin cancer is required. This study aimed to apply a follower-leading clustering algorithm to classify CBCA and article themes and present articles that deserve reading in recent ten years.
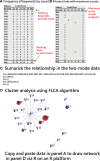
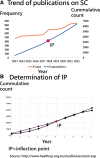
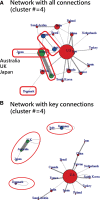
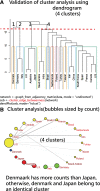
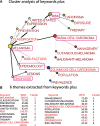
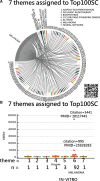
Methods: Between 2013 and 2022, a total of 6526 articles focusing on SC were extracted from the Web of Science core collection. The descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics model was employed to visualize the study results. Various visualizations, including 4-quadrant radar plots, line charts, scatter plots, network charts, chord diagrams, and impact beam plots, were utilized. The category, journal, authorship, and L-index score were employed to assess individual research achievements. Diagnostic analytics were used to cluster the CBCA and identify common article themes. Keyword weights were utilized to predict article citations, and noteworthy articles were highlighted in prescriptive analytics based on the 100 most highly cited articles on SC (T100SC).
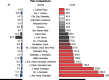
Results: The primary entities contributing to SC research include the United States, the University of California, San Francisco in US, dermatology department, and the author Andreas Stang from Germany, who possess higher category, journal, authorship, and L-index scores. The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology has published the highest number of articles (n = 336, accounting for 5.16% of the total). From the T100SC, 7 distinct themes were identified, with melanoma being the predominant theme (92% representation). A strong correlation was observed between the number of article citations and the keyword weights (F = 81.63; P < .0001). Two articles with the highest citation counts were recommended for reading.
Conclusion: By applying the descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics model, 2 noteworthy articles were identified and highlighted on an impact beam plot. These articles are considered deserving of attention and could potentially inspire further research in the field of bibliometrics, focusing on relevant topics related to melanoma.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The model of descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics on 100 top-cited articles of nasopharyngeal carcinoma from 2013 to 2022: Bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Feb 10;102(6):e32824. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032824. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36820592 Free PMC article.
-
Classification and citation analysis of the 100 top-cited articles on nurse resilience using chord diagrams: A bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Mar 17;102(11):e33191. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033191. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36930064 Free PMC article.
-
A leading bibliometric author does not have a dominant contribution to research based on the CJAL score: Bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jan 13;102(2):e32609. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032609. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36637941 Free PMC article.
-
Thematic analysis of articles on artificial intelligence with spine trauma, vertebral metastasis, and osteoporosis using chord diagrams: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 30;101(52):e32369. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032369. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36596060 Free PMC article.
-
Global research trends in artificial intelligence for critical care with a focus on chord network charts: Bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 22;102(38):e35082. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035082. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37746962 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnold M, Kvaskoff M, Thuret A, et al. . Cutaneous melanoma in France in 2015 attributable to solar ultraviolet radiation and the use of sunbeds. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:1681–6. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, de Vries E, Whiteman DC, et al. . Global burden of cutaneous melanoma attributable to ultraviolet radiation in 2012. Int J Cancer. 2018;143:1305–14. - PubMed
-
- Islami F, Sauer AG, Miller KD, et al. . Cutaneous melanomas attributable to ultraviolet radiation exposure by state. Int J Cancer. 2020;147:1385–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

