Successful Treatment of Concurrent Follicular Lymphoma and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Using Rituximab Plus Nab-Paclitaxel and Cisplatin: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 37933332
- PMCID: PMC10625777
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S430273
Successful Treatment of Concurrent Follicular Lymphoma and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Using Rituximab Plus Nab-Paclitaxel and Cisplatin: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
Background: Co-occurrence of breast cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is a rare condition with diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. The coexistence of follicular lymphoma (FL) and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) has not been described previously.
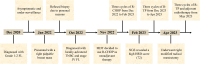
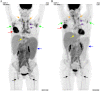
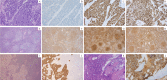
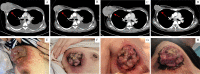
Case presentation: A 46-year-old woman, already suffering a history of untreated, advanced-stage, high tumor burden FL, was admitted for a rapidly progressing right breast mass. Ultrasonography showed an 8.3 × 3.6 × 4.1 cm fungating mass in the right breast with enlarged lymph nodes (LNs) in bilateral axillae. PET-CT demonstrated increased 18F- FDG activity in right breast mass, LNs on both sides of the diaphragm, enlarged spleen, and bone marrow. Biopsy of the right breast mass revealed TNBC. The patient underwent neoadjuvant therapy with R-CHOP and achieved partial response of breast tumor. However, TNBC progressed after three cycles of R-CHOP. According to the next-generation sequencing (NGS) assay on breast mass showing a homologous recombination repair (HRR) deficiency (HRD) score of 72, the neoadjuvant regimen was changed to rituximab plus nab-paclitaxel and cisplatin (R-TP) and resulted in significant tumor regression. The patient then underwent right mastectomy with an axillary LN dissection. After the surgery, she was regularly monitored and given adjuvant therapy with R-TP and radiotherapy.
Conclusion: The coexistence of FL and HRD-positive TNBC poses diagnostic and treatment challenges. Well-founded neoadjuvant strategy based on multidisciplinary team (MDT) discussion and NGS warranted a good outcome in this case.
Keywords: HRD; MDT; case report; follicular lymphoma; multiple primary malignancies; neoadjuvant therapy; triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2023 Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

