Common Peroneal Nerve Compression Neuropathy Due to a Large Synovial Cyst From the Proximal Tibiofibular Joint in a Teenager
- PMID: 37933352
- PMCID: PMC10625661
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.46562
Common Peroneal Nerve Compression Neuropathy Due to a Large Synovial Cyst From the Proximal Tibiofibular Joint in a Teenager
Abstract
Ganglion cysts are very rare in the lower limb and when present, ganglion cysts rarely cause compression neuropathy at any site. Peripheral nerve sheath tumors as a whole, are also very rare and mostly presented as a painful lump along the nerve path. Ganglion cysts are non-neoplastic gelatinous cysts, which lack true synovial lining. They can be divided into intraneural cysts which can be found within the epineurium of a peripheral nerve and lead to signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy or extraneural cysts which can develop from surrounding joints or tendon sheaths causing gradual nerve compression. Intraneural tumors of common peroneal nerve (CPN) are widely reported in the literature with varying degrees of symptoms; however, there are only a few case reports describing CPN palsy due to extraneural cysts. We are reporting a rare case of atraumatic CPN palsy, which resulted in irreversible foot drop in a teenage boy who presented with right leg radiating calf and foot pain. We recommend prompt investigation and excision of the cyst to decompress the nerve to increase the chances of early recovery and favorable outcomes.
Keywords: common peroneal neuropathy; foot drop; knee ganglion cyst; ortho surgery; rare tumors.
Copyright © 2023, Khalefa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
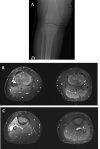
Figures

References
-
- Nerve tumors of the hand and forearm. Strickland JW, Steichen JB. J Hand Surg Am. 1977;2:285–291. - PubMed
-
- Ganglion der Nervenscheide des Nervus peroneus. Sultan C. http://www.scirp.org/(S(lz5mqp453edsnp55rrgjct55))/reference/ReferencesP... Zentralblatt fur Chirurgie. Zentralbl Chir. 1921;48:963–965.
-
- Intraneural ganglion of the superficial peroneal nerve: a case report. Stamatis ED, Manidakis NE, Patouras PP. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2010;49:400–404. - PubMed
-
- Peroneal nerve palsy secondary to ganglion cyst of the proximal tibiofibular joint in a pediatric patient. Frank DA, Sangimino MJ. Orthopedics. 2008;31:86. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
