Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in primary Meige syndrome: motor and non-motor outcomes
- PMID: 37933887
- PMCID: PMC11235968
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.16121
Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in primary Meige syndrome: motor and non-motor outcomes
Abstract
Background and purpose: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has emerged as a promising treatment for movement disorders. This prospective study aims to evaluate the effects of bilateral subthalamic nucleus DBS (STN-DBS) on motor and non-motor symptoms in patients with primary Meige syndrome.
Methods: Thirty patients who underwent bilateral STN-DBS between April 2017 and June 2020 were included. Standardized and validated scales were utilized to assess the severity of dystonia, health-related quality of life, sleep, cognitive function and mental status at baseline and at 1 year and 3 years after neurostimulation.
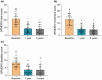
Results: The Burke-Fahn-Marsden Dystonia Rating Scale movement scores showed a mean improvement of 63.0% and 66.8% at 1 year and 3 years, respectively, after neurostimulation. Similarly, the Burke-Fahn-Marsden Dystonia Rating Scale disability scores improved by 60.8% and 63.3% at the same time points. Postoperative quality of life demonstrated a significant and sustained improvement throughout the follow-up period. However, cognitive function, mental status, sleep quality and other neuropsychological functions did not change after 3 years of neurostimulation. Eight adverse events occurred in six patients, but no deaths or permanent sequelae were reported.
Conclusions: Bilateral STN-DBS is a safe and effective alternative treatment for primary Meige syndrome, leading to improvements in motor function and quality of life. Nevertheless, it did not yield significant amelioration in cognitive, mental, sleep status and other neuropsychological functions after 3 years of neurostimulation.
Keywords: Meige syndrome; deep brain stimulation; dystonia; non-motor symptoms; subthalamic nucleus.
© 2023 The Authors. European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bilateral Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation in Meige Syndrome: Effects on Motor Function, Neuropsychological Status, and Mood.Neurosurgery. 2023 May 1;92(5):1073-1079. doi: 10.1227/neu.0000000000002335. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Neurosurgery. 2023. PMID: 36728352
-
Bilateral deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in primary Meige syndrome.J Neurosurg. 2018 Mar;128(3):897-902. doi: 10.3171/2016.12.JNS16383. Epub 2017 May 26. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28548593
-
Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for primary Meige syndrome: clinical outcomes and predictive factors.J Neurosurg. 2024 Jan 19;140(6):1650-1663. doi: 10.3171/2023.11.JNS232075. Print 2024 Jun 1. J Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 38241667
-
Subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus internus deep brain stimulation in the treatment of dystonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of safety and efficacy.J Clin Neurosci. 2025 Feb;132:110958. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2024.110958. Epub 2024 Dec 7. J Clin Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39647323
-
Long-term follow-up of deep brain stimulation for Meige syndrome.Neurosurg Focus. 2010 Aug;29(2):E5. doi: 10.3171/2010.4.FOCUS1067. Neurosurg Focus. 2010. PMID: 20672922 Review.
Cited by
-
Putaminal-cortical circuits predict response of bilateral deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in the primary Meige syndrome after 5 years.Brain Commun. 2025 Feb 8;7(1):fcaf042. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaf042. eCollection 2025. Brain Commun. 2025. PMID: 39944744 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained quality-of-life improvements over 10 years after subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for isolated dystonia.J Neurol. 2025 Jan 7;272(1):92. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12820-4. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39776258
-
Development and Validation of a Nomogram Based on Inflammatory Markers for Risk Prediction in Meige Syndrome Patients.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct 25;17:7721-7731. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S481649. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39473982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balint B, Mencacci NE, Valente EM, et al. Dystonia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:25. - PubMed
-
- Pandey S, Sharma S. Meige's syndrome: history, epidemiology, clinical features, pathogenesis and treatment. J Neurol Sci. 2017;372:162‐170. - PubMed
-
- Jochim A, Meindl T, Huber C, et al. Treatment of blepharospasm and Meige's syndrome with abo‐ and onabotulinumtoxinA: long‐term safety and efficacy in daily clinical practice. J Neurol. 2020;267:267‐275. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

