CCDC15 localizes to the centriole inner scaffold and controls centriole length and integrity
- PMID: 37934472
- PMCID: PMC10630097
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202305009
CCDC15 localizes to the centriole inner scaffold and controls centriole length and integrity
Abstract
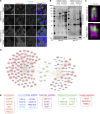
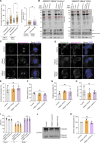
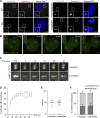
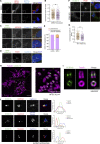
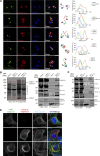
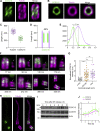
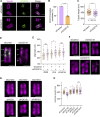
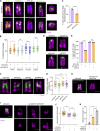
Centrioles are microtubule-based organelles responsible for forming centrosomes and cilia, which serve as microtubule-organizing, signaling, and motility centers. Biogenesis and maintenance of centrioles with proper number, size, and architecture are vital for their functions during development and physiology. While centriole number control has been well-studied, less is understood about their maintenance as stable structures with conserved size and architecture during cell division and ciliary motility. Here, we identified CCDC15 as a centriole protein that colocalizes with and interacts with the inner scaffold, a crucial centriolar subcompartment for centriole size control and integrity. Using ultrastructure expansion microscopy, we found that CCDC15 depletion affects centriole length and integrity, leading to defective cilium formation, maintenance, and response to Hedgehog signaling. Moreover, loss-of-function experiments showed CCDC15's role in recruiting both the inner scaffold protein POC1B and the distal SFI1/Centrin-2 complex to centrioles. Our findings reveal players and mechanisms of centriole architectural integrity and insights into diseases linked to centriolar defects.
© 2023 Arslanhan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Aydogan, M.G., Hankins L.E., Steinacker T.L., Mofatteh M., Saurya S., Wainman A., Wong S.S., Lu X., Zhou F.Y., and Raff J.W.. 2022. Centriole distal-end proteins CP110 and Cep97 influence centriole cartwheel growth at the proximal end. J. Cell Sci. 135:jcs260015. 10.1242/jcs.260015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

