Association between Obesity and Periodontitis in US Adults: NHANES 2011-2014
- PMID: 37935140
- PMCID: PMC10836934
- DOI: 10.1159/000534751
Association between Obesity and Periodontitis in US Adults: NHANES 2011-2014
Abstract
Introduction: It is controversial whether obesity and periodontitis are related. A representative US population was examined for the relationship between obesity and periodontitis.
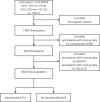
Methods: In the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2011-2014, participants (n = 6,662) aged 30 years or older and who underwent periodontal examinations were chosen for analysis. An assessment of obesity was based on body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC). Estimates of obesity and periodontal disease were made using univariate and multivariate logistic regression models.
Results: According to an adjusted odds ratio (OR) for periodontitis, BMI (OR = 1.01, 95% CI: 1.01∼1.02) and WC (OR = 1.01, 95% CI: 1∼1.01) were significantly associated with periodontitis, respectively. After adjusting for confounding factors, the OR for patients with high WC with periodontitis was 1.18 (1.04∼1.33) compared to normal WC. BMI and WC subgroups showed no significant interaction (p for interaction >0.05), except for the age interaction in BMI. Among young adults aged 30-44 years, obesity was significantly associated with periodontitis in subgroups; the adjusted OR for having periodontal disease was 1.02 (1∼1.03) and 1.01 (1∼1.02) for subjects with BMI and WC, respectively. When all covariates were adjusted, BMI ≥30 kg/m2 was statistically significantly associated with prevalence of periodontal disease among people aged 30-44 years (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: BMI and WC are significantly associated with periodontitis, even after adjusting for many variables, and were equally significant in obese (BMI ≥30 kg/m2) young people (30-44 years).
Keywords: Body mass index; National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; Obesity; Periodontitis; Waist circumference.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sci-Hub | Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. Available from: https://www.sci-hub.se/10.1038/s41574-019-0176-8 (accessed May 8, 2023). - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dixon JB. The effect of obesity on health outcomes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;316(2):104–8. - PubMed
-
- Tibúrcio-Machado CS, Michelon C, Zanatta FB, Gomes MS, Marin JA, Bier CA. The global prevalence of apical periodontitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Endod J. 2021;54(5):712–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

