Low-temperature hydroformylation of ethylene by phosphorous stabilized Rh sites in a one-pot synthesized Rh-(O)-P-MFI zeolite
- PMID: 37935688
- PMCID: PMC10630368
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42938-4
Low-temperature hydroformylation of ethylene by phosphorous stabilized Rh sites in a one-pot synthesized Rh-(O)-P-MFI zeolite
Abstract
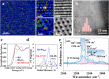
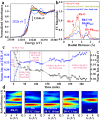
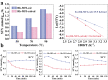
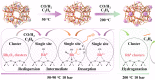
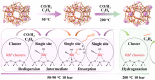
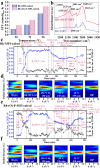
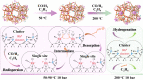
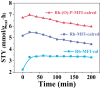
Zeolites containing Rh single sites stabilized by phosphorous were prepared through a one-pot synthesis method and are shown to have superior activity and selectivity for ethylene hydroformylation at low temperature (50 °C). Catalytic activity is ascribed to confined Rh2O3 clusters in the zeolite which evolve under reaction conditions into single Rh3+ sites. These Rh3+ sites are effectively stabilized in a Rh-(O)-P structure by using tetraethylphosphonium hydroxide as a template, which generates in situ phosphate species after H2 activation. In contrast to Rh2O3, confined Rh0 clusters appear less active in propanal production and ultimately transform into Rh(I)(CO)2 under similar reaction conditions. As a result, we show that it is possible to reduce the temperature of ethylene hydroformylation with a solid catalyst down to 50 °C, with good activity and high selectivity, by controlling the electronic and morphological properties of Rh species and the reaction conditions.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Yan G, et al. Reaction product-driven restructuring and assisted stabilization of a highly dispersed Rh-on-ceria catalyst. Nat. Catal. 2022;5:119–127. doi: 10.1038/s41929-022-00741-2. - DOI
-
- Finzel J, et al. Limits of detection for EXAFS characterization of heterogeneous single-atom catalysts. ACS Catal. 2023;13:6462–6473. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.3c01116. - DOI
-
- van Deelen TW, Hernández Mejía C, de Jong KP. Control of metal-support interactions in heterogeneous catalysts to enhance activity and selectivity. Nat. Catal. 2019;2:955–970. doi: 10.1038/s41929-019-0364-x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

