Prediction of pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia
- PMID: 37935890
- PMCID: PMC10630265
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-023-01199-6
Prediction of pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia
Abstract
Background: Predictors of ICU-acquired pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) are not well-established in critically ill patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), making IPA commonly misdiagnosed and anti-fungal therapy delayed. We aimed to develop a clinical score for prediction of IPA among patients with VAP.
Methods: Mechanically ventilated patients who developed VAP in 4 ICUs in Bretagne, Western France, were included. The score was constructed in a learning cohort, based on predictors of IPA in logistic regression model, and validated in a validation cohort.
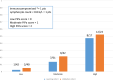
Results: Among 1636 mechanically ventilated patients, 215 developed VAP but only 39 developed IPA (4 possible and 35 probable/putative) (18%). Most cases (31/39) were documented through a positive broncho-alveolar sample culture. Independent predictors of IPA were immunodepression (including onco-hematological disorder, immunomodulatory treatment, solid organ transplant, neutropenia < 0.5G/L and high-dose steroids ≥ 1 mg/kg/day of prednisolone equivalent) (p = 0.001; score = 1 point) and lymphocyte count at admission < 0.8 G/L (p = 0.019; score = 1 point). Operational values of the predictive score in the learning/validation cohort were 50%/52% sensitivity and 90%/87% specificity, respectively, for high PiPa score (score = 2) and 94%/91% sensitivity and 44%/46% specificity, respectively, for moderate PiPa score (score = 1). Finally, the AUC for the prediction of IPA was 0.783 in the learning cohort and 0.770 in the validation cohort.
Conclusions: We evaluated a clinical score with good predictive value which may help to predict IPA in patient with VAP. External validation will be needed to confirm our preliminary findings.
Keywords: Acquired infection; Critical care; Pneumonia; Prediction score; Pulmonary aspergillosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- - Blot SI, Taccone FS, Van den Abeele AM, Bulpa P, et al. A clinical algorithm to diagnose invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186(1):56–64. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201111-1978OC. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Erratum in: Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186(8):808. PMID: 22517788. - PubMed
-
- - Rodriguez-Goncer I, Thomas S, Foden P, et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is associated with adverse clinical outcomes in critically ill patients receiving veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Jul;37(7):1251–1257. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-3241-7. Epub 2018 Apr 6. PMID: 29623451; PMCID: PMC6015116. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources