Efficacy of therapeutic drug monitoring-based antibiotic regimen in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 37936203
- PMCID: PMC10631080
- DOI: 10.1186/s40560-023-00699-8
Efficacy of therapeutic drug monitoring-based antibiotic regimen in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM)-based antimicrobial dosing optimization strategies on pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics and specific drug properties for critically ill patients is unclear. Here, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to evaluate the effectiveness of TDM-based regimen in these patients.
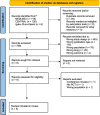
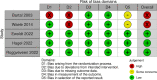
Methods: Articles from three databases were systematically retrieved to identify relevant randomized control studies. Version two of the Cochrane tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized trials was used to assess the risk of bias in studies included in the analysis, and quality assessment of evidence was graded using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation approach. Primary outcome was the 28-day mortality and secondary outcome were in-hospital mortality, clinical cure, length of stay in the intensive care unit (ICU) and target attainment at day 1 and 3.
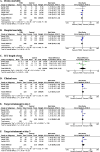
Results: In total, 5 studies involving 1011 patients were included for meta-analysis of the primary outcome, of which no significant difference was observed between TDM-based regimen and control groups (risk ratio [RR] 0.94, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.77-1.14; I2 = 0%). In-hospital mortality (RR 0.96, 95% CI: 0.76-1.20), clinical cure (RR 1.23, 95% CI: 0.91-1.67), length of stay in the ICU (mean difference 0, 95% CI: - 2.18-2.19), and target attainment at day 1 (RR 1.14, 95% CI: 0.88-1.48) and day 3 (RR 1.35, 95% CI: 0.90-2.03) were not significantly different between the two groups, and all evidence for the secondary outcomes had a low or very low level of certainty because the included studies had serious risk of bias, variation of definition for outcomes, and small sample sizes.
Conclusion: TDM-based regimens had no significant efficacy for clinical or pharmacological outcomes. Further studies with other achievable targets and well-defined outcomes are required.
Trial registration: Clinical trial registration; PROSPERO ( https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/ ), registry number: CRD 42022371959. Registered 24 November 2022.
Keywords: Antibiotics; Pharmacodynamics; Pharmacokinetics; Sepsis; TDM.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beta-Lactam Antibiotic Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Nov 14;75(10):1848-1860. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac506. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35731853 Free PMC article.
-
Early versus late initiation of renal replacement therapy in patients with acute kidney injury-a systematic review & meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Feb 28;18(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0486-9. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28245793 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol-directed sedation versus non-protocol-directed sedation in mechanically ventilated intensive care adults and children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 12;11(11):CD009771. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009771.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30480753 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorhexidine bathing of the critically ill for the prevention of hospital-acquired infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Aug 30;8(8):CD012248. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012248.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31476022 Free PMC article.
-
Early enteral nutrition within 24 hours of lower gastrointestinal surgery versus later commencement for length of hospital stay and postoperative complications.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jul 22;7(7):CD004080. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004080.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31329285 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence to Close the Gap between Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Targets and Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Narrative Review on Beta Lactams.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Sep 6;13(9):853. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13090853. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of the practical impact of adjusting beta-lactam dosages based on therapeutic drug monitoring in critically ill adult patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials and observational studies.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 2;14(1):7793. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58200-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38565898 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug-Resistant Infections and Metabolic Syndrome: An Overlooked Bidirectional Relationship.Biomedicines. 2025 May 30;13(6):1343. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061343. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk Factors Associated with Antibiotic Exposure Variability in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Aug 24;13(9):801. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13090801. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiotic Therapy Duration for Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections: An Evidence-Based Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 18;26(14):6905. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146905. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725151 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

