A comparative study on the features of breast sclerosing adenosis and invasive ductal carcinoma via ultrasound and establishment of a predictive nomogram
- PMID: 37936612
- PMCID: PMC10627161
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1276524
A comparative study on the features of breast sclerosing adenosis and invasive ductal carcinoma via ultrasound and establishment of a predictive nomogram
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the clinical and ultrasonic characteristics of breast sclerosing adenosis (SA) and invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), and construct a predictive nomogram for SA.
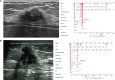
Materials and methods: A total of 865 patients were recruited at the Second Hospital of Shandong University from January 2016 to November 2022. All patients underwent routine breast ultrasound examinations before surgery, and the diagnosis was confirmed by histopathological examination following the operation. Ultrasonic features were recorded using the Breast Imaging Data and Reporting System (BI-RADS). Of the 865 patients, 203 (252 nodules) were diagnosed as SA and 662 (731 nodules) as IDC. They were randomly divided into a training set and a validation set at a ratio of 6:4. Lastly, the difference in clinical characteristics and ultrasonic features were comparatively analyzed.
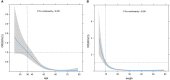
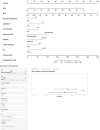
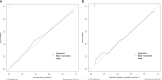
Result: There was a statistically significant difference in multiple clinical and ultrasonic features between SA and IDC (P<0.05). As age and lesion size increased, the probability of SA significantly decreased, with a cut-off value of 36 years old and 10 mm, respectively. In the logistic regression analysis of the training set, age, nodule size, menopausal status, clinical symptoms, palpability of lesions, margins, internal echo, color Doppler flow imaging (CDFI) grading, and resistance index (RI) were statistically significant (P<0.05). These indicators were included in the static and dynamic nomogram model, which showed high predictive performance, calibration and clinical value in both the training and validation sets.
Conclusion: SA should be suspected in asymptomatic young women, especially those younger than 36 years of age, who present with small-size lesions (especially less than 10 mm) with distinct margins, homogeneous internal echo, and lack of blood supply. The nomogram model can provide a more convenient tool for clinicians.
Keywords: BI-RADS; invasive ductal carcinoma; nomogram; sclerosing adenosis; ultrasonic features.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Wei, Pang, Ni, Wu, Xiao, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multimodal ultrasound imaging for diagnostic differentiation of sclerosing adenosis from invasive ductal carcinoma.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):877-887. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-524. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38223094 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics Based on DCE-MRI Improved Diagnostic Performance Compared to BI-RADS Analysis in Identifying Sclerosing Adenosis of the Breast.Front Oncol. 2022 May 12;12:888141. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.888141. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35646630 Free PMC article.
-
An ultrasound-based radiomics model to distinguish between sclerosing adenosis and invasive ductal carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 7;13:1090617. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1090617. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36959807 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound characteristics of sclerosing adenosis mimicking breast carcinoma.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 May;181(1):127-134. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05609-2. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32227257
-
Value of multimodal imaging in the diagnosis of breast sclerosing adenosis associated with malignant lesions.J Clin Ultrasound. 2023 Mar;51(3):485-493. doi: 10.1002/jcu.23376. Epub 2022 Oct 17. J Clin Ultrasound. 2023. PMID: 36250329
Cited by
-
Developing ultrasound-based machine learning models for accurate differentiation between sclerosing adenosis and invasive ductal carcinoma.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11777-w. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40581674
-
The Prediction Model of High-Frequency Ultrasound Combined with Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Scoring System Improved the Diagnosis of Sclerosing Adenosis and Early Breast Cancer.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2025 Feb 7;17:145-155. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S483496. eCollection 2025. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2025. PMID: 39936075 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-based comparative analysis and nomogram development for predicting triple-negative and non-triple-negative breast cancer: a 4-year institutional study in Quanzhou First Hospital.BMJ Open. 2024 Jun 13;14(6):e085340. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-085340. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38871659 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Su X, Lin Q, Cui C, Xu W, Wei Z, Fei J, et al. . Non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: comparison of diagnostic accuracy of digital breast tomosynthesis, digital mammography, and ultrasonography. Breast Cancer (Tokyo Japan) (2017) 24(4):562–70. doi: 10.1007/s12282-016-0739-7 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

