Crystal structure and supra-molecular features of a bis-urea-functionalized pillar[5]arene
- PMID: 37936859
- PMCID: PMC10626966
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023009003
Crystal structure and supra-molecular features of a bis-urea-functionalized pillar[5]arene
Abstract
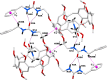
The crystal structure of a bis-urea derivative based on A1/A2-functionalized pillar[5]arene (DUP) that encapsulates dimethyl formamide (DMF) inside the macrocyclic cavity is reported. The crystal structure of DUP·DMF, C63H70N4O12·C3H7NO, reveals that out of two urea functionalized spacers, one arm is oriented above the macrocyclic cavity with strong hydrogen-bonding inter-actions between the urea H atoms and DMF guest, whereas, the other arm is positioned away from the macrocycle, leading to inter-molecular hydrogen-bonding inter-actions between the urea H atoms of two adjacent pillar[5]arene macrocycles, resulting in the formation of a supra-molecular dimer.
Keywords: crystal structure; dimer; pillararene; receptor; urea substitution.
© Vinodh et al. 2023.
Figures



References
-
- Bi, J., Zeng, X., Tian, D. & Li, H. (2016). Org. Lett. 18, 1092–1095. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, M., Wang, Q., Cao, Y., Pan, Y., Yang, Z., Jiang, J. & Wang, L. (2016). Tetrahedron Lett. 57, 4133–4137.
-
- Deng, H., Shu, X., Hu, X., Li, J., Jia, X. & Li, C. (2012). Tetrahedron Lett. 53, 4609–4612.
-
- Duan, Q., Xia, W., Hu, X., Ni, M., Jiang, J., Lin, C., Pan, Y. & Wang, L. (2012). Chem. Commun. 48, 8532–8534. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
