Effectiveness of Thromboprophylaxis Agents Following Hip Fracture: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37936980
- PMCID: PMC10624462
- DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.OA.23.00064
Effectiveness of Thromboprophylaxis Agents Following Hip Fracture: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Multiple studies have compared different pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis agents after hip fracture surgery, including aspirin, unfractionated heparin (UFH), low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH), direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC), and warfarin, resulting in variability in clinical practice. To guide clinical management, a systematic review and network meta-analysis (NMA), which enables the simultaneous assessment of the effects of multiple interventions for the same patient population, was performed. This study aimed to determine the comparative effectiveness of thromboprophylaxis in reducing venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with surgically treated hip fractures.
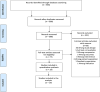
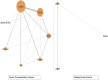
Methods: The primary outcome was the effect of the treatment on the VTE rate, and the secondary outcome was the treatment effect on the bleeding rate. Relevant studies were identified by a systematic search of Embase, MEDLINE, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) from January 2000 to February 2022. Title, abstract, and full-text screening; data extraction; and risk-of-bias assessment were performed. All studies examining thromboprophylaxis interventions (DOAC, LMWH, UFH, aspirin, and warfarin) in patients with a surgically treated hip fracture were included. Bayesian NMA was performed, and dichotomous outcome data were pooled using the odds ratio. Interventions were ranked using the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) for each outcome.
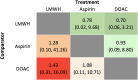
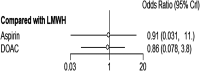
Results: A total of 19 studies were included after the screening of 466 citations and 77 full-text articles. Of the included studies, 15 studies had a high overall risk of bias. The NMA of the VTE outcome included 19 studies, 49,409 participants, and 6 thromboprophylaxis interventions. The NMA of the bleeding outcome included 3 studies, 18,163 participants, and 3 interventions. The mean age ranged from 43.5 to 86.2 years among the included studies. No thromboprophylaxis intervention was statistically different from any other intervention in its effect on the VTE or bleeding rate in hip fracture patients.
Conclusions: This NMA demonstrated that there was no difference between the thromboprophylaxis interventions in reducing VTE or bleeding rates in hip fracture patients. More robust randomized controlled trials are needed to determine the most effective thromboprophylaxis interventions for patients with hip fractures.
Level of evidence: Therapeutic Level II. See Instructions for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Goodpaster BH, Park SW, Harris TB, Kritchevsky SB, Nevitt M, Schwartz AV, Simonsick EM, Tylavsky FA, Visser M, Newman AB. The loss of skeletal muscle strength, mass, and quality in older adults: the health, aging and body composition study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006. Oct;61(10):1059-64. - PubMed
-
- MacDougall DA, Feliu AL, Boccuzzi SJ, Lin J. Economic burden of deep-vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and post-thrombotic syndrome. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006. Oct 15;63(20)(Suppl 6):S5-15. - PubMed
-
- Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, Heit JA, Samama CM, Lassen MR, Colwell CW. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008. Jun;133(6)(Suppl):381S-453S. - PubMed
-
- Falck-Ytter Y, Francis CW, Johanson NA, Curley C, Dahl OE, Schulman S, Ortel TL, Pauker SG, Colwell CW, Jr. Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012. Feb;141(2)(Suppl):e278S-325S. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
