A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 2: host extracellular to systemic effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 37938797
- PMCID: PMC10772081
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-023-01462-1
A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 2: host extracellular to systemic effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
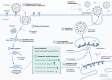
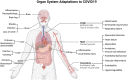
COVID-19, the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, has caused significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. The betacoronavirus continues to evolve with global health implications as we race to learn more to curb its transmission, evolution, and sequelae. The focus of this review, the second of a three-part series, is on the biological effects of the SARS-CoV-2 virus on post-acute disease in the context of tissue and organ adaptations and damage. We highlight the current knowledge and describe how virological, animal, and clinical studies have shed light on the mechanisms driving the varied clinical diagnoses and observations of COVID-19 patients. Moreover, we describe how investigations into SARS-CoV-2 effects have informed the understanding of viral pathogenesis and provide innovative pathways for future research on the mechanisms of viral diseases.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
RES is on the scientific advisory board of Miromatrix Inc and Lime Therapeutics and is a consultant and speaker for Alnylam Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 1: Intracellular overdrive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.Eur J Hum Genet. 2022 Aug;30(8):889-898. doi: 10.1038/s41431-022-01108-8. Epub 2022 May 16. Eur J Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 35577935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From People to Panthera: Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Tigers and Lions at the Bronx Zoo.mBio. 2020 Oct 13;11(5):e02220-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02220-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33051368 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Pathol. 2020 Jul;251(3):228-248. doi: 10.1002/path.5471. Epub 2020 Jun 10. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32418199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and research gaps: Understanding SARS-CoV-2 interaction with the ACE2 receptor and implications for therapy.Theranostics. 2020 Jun 12;10(16):7448-7464. doi: 10.7150/thno.48076. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32642005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneity in transmissibility and shedding SARS-CoV-2 via droplets and aerosols.Elife. 2021 Apr 16;10:e65774. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65774. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33861198 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Circulating Antibodies Against Common Cold Coronaviruses Do Not Interfere with Immune Responses to Primary or Booster SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 May 21;13(5):547. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13050547. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40432156 Free PMC article.
-
The metabolic footprint of Vero E6 cells highlights the key metabolic routes associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and response to drug combinations.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 4;14(1):7950. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57726-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38575586 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of COVID-19 virus-like particles on the behavioral and cognitive performance of human apolipoprotein E targeted replacement mice.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 26;15:1473366. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1473366. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39660133 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired immune responses in the airways are associated with poor outcome in critically ill COVID-19 patients.ERJ Open Res. 2024 Jul 8;10(4):00789-2023. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00789-2023. eCollection 2024 Jul. ERJ Open Res. 2024. PMID: 38978558 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers in Infectious Diseases.Biology (Basel). 2025 Feb 11;14(2):182. doi: 10.3390/biology14020182. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rydland HT, Friedman J, Stringhini S, Link BG, Eikemo TA. The radically unequal distribution of Covid-19 vaccinations: a predictable yet avoidable symptom of the fundamental causes of inequality. Humanit Soc Sci Commun. 2022;9:1–16.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

