Correlates of Risk for Disinhibited Behaviors in the Million Veteran Program Cohort
- PMID: 37938835
- PMCID: PMC10633411
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2023.4141
Correlates of Risk for Disinhibited Behaviors in the Million Veteran Program Cohort
Abstract
Importance: Many psychiatric outcomes share a common etiologic pathway reflecting behavioral disinhibition, generally referred to as externalizing (EXT) disorders. Recent genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have demonstrated the overlap between EXT disorders and important aspects of veterans' health, such as suicide-related behaviors and substance use disorders (SUDs).
Objective: To explore correlates of risk for EXT disorders within the Veterans Health Administration (VA) Million Veteran Program (MVP).
Design, setting, and participants: A series of phenome-wide association studies (PheWASs) of polygenic risk scores (PGSs) for EXT disorders was conducted using electronic health records. First, ancestry-specific PheWASs of EXT PGSs were conducted in the African, European, and Hispanic or Latin American ancestries. Next, a conditional PheWAS, covarying for PGSs of comorbid psychiatric problems (depression, schizophrenia, and suicide attempt; European ancestries only), was performed. Lastly, to adjust for unmeasured confounders, a within-family analysis of significant associations from the main PheWAS was performed in full siblings (European ancestries only). This study included the electronic health record data from US veterans from VA health care centers enrolled in MVP. Analyses took place from February 2022 to August 2023 covering a period from October 1999 to January 2020.
Exposures: PGSs for EXT, depression, schizophrenia, and suicide attempt.
Main outcomes and measures: Phecodes for diagnoses derived from the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Ninth and Tenth Revisions, Clinical Modification, codes from electronic health records.
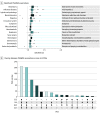
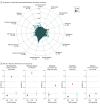
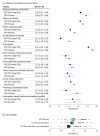
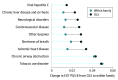
Results: Within the MVP (560 824 patients; mean [SD] age, 67.9 [14.3] years; 512 593 male [91.4%]), the EXT PGS was associated with 619 outcomes, of which 188 were independent of risk for comorbid problems or PGSs (from odds ratio [OR], 1.02; 95% CI, 1.01-1.03 for overweight/obesity to OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.42-1.47 for viral hepatitis C). Of the significant outcomes, 73 (11.9%) were significant in the African results and 26 (4.5%) were significant in the Hispanic or Latin American results. Within-family analyses uncovered robust associations between EXT PGS and consequences of SUDs, including liver disease, chronic airway obstruction, and viral hepatitis C.
Conclusions and relevance: Results of this cohort study suggest a shared polygenic basis of EXT disorders, independent of risk for other psychiatric problems. In addition, this study found associations between EXT PGS and diagnoses related to SUDs and their sequelae. Overall, this study highlighted the potential negative consequences of EXT disorders for health and functioning in the US veteran population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Update of
-
Correlates of Risk for Disinhibited Behaviors in the Million Veteran Program Cohort.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 11:2023.03.22.23286865. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.22.23286865. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: JAMA Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 1;81(2):188-197. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2023.4141. PMID: 37034805 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ferrari A; GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators . Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022;9(2):137-150. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00395-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reitsma MB, Fullman N, Ng M, et al. ; GBD 2015 Tobacco Collaborators . Smoking prevalence and attributable disease burden in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2017;389(10082):1885-1906. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30819-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Degenhardt L, Charlson F, Ferrari A, et al. ; GBD 2016 Alcohol and Drug Use Collaborators . The global burden of disease attributable to alcohol and drug use in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018;5(12):987-1012. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30337-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

