Identification of natural antiviral drug candidates against Tilapia Lake Virus: Computational drug design approaches
- PMID: 37939069
- PMCID: PMC10631680
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287944
Identification of natural antiviral drug candidates against Tilapia Lake Virus: Computational drug design approaches
Abstract
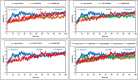
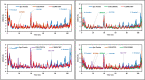
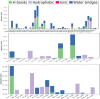
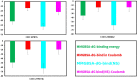
Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) is a disease that affects tilapia fish, causing a high rate of sudden death at any stage in their life cycle. Unfortunately, there are currently no effective antiviral drugs or vaccines to prevent or control the progression of this disease. Researchers have discovered that the CRM1 protein plays a critical function in the development and spreading of animal viruses. By inhibiting CRM1, the virus's spread in commercial fish farms can be suppressed. With this in mind, this study intended to identify potential antiviral drugs from two different tropical mangrove plants from tropical regions: Heritiera fomes and Ceriops candolleana. To identify promising compounds that target the CRM1 protein, a computer-aided drug discovery approach is employed containing molecular docking, ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion) analysis, toxicity assessment as well as molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. To estimate binding affinities of all phytochemicals, molecular docking is used and the top three candidate compounds with the highest docking scores were selected, which are CID107876 (-8.3 Kcal/mol), CID12795736 (-8.2 Kcal/mol), and CID12303662 (-7.9 Kcal/mol). We also evaluated the ADME and toxicity properties of these compounds. Finally, MD simulation was conducted to analyze the stability of the protein-ligand complex structures and confirm the suitability of these compounds. The computational study demonstrated that the phytochemicals found in H. fomes and C. candolleana could potentially serve as important inhibitors of TiLV, offering practical utility. However, further in vivo investigations are necessary to investigate and potentially confirm the effectiveness of these compounds as antiviral drugs against the virus TiLV.
Copyright: © 2023 Sumon et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests.
Figures
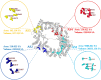

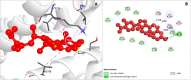
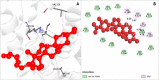
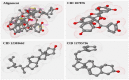

Similar articles
-
Compounds Identified from Marine Mangrove Plant (Avicennia alba) as Potential Antiviral Drug Candidates Against WDSV, an In-Silico Approach.Mar Drugs. 2021 Apr 28;19(5):253. doi: 10.3390/md19050253. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33925208 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Phage Display Technology with In Silico-Designed Epitope Vaccine to Elicit Robust Antibody Responses against Emerging Pathogen Tilapia Lake Virus.J Virol. 2023 Apr 27;97(4):e0005023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00050-23. Epub 2023 Mar 28. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 36975794 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Characterization of Open Reading Frame-Encoded Functional Genes from Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV).Mol Biotechnol. 2019 Dec;61(12):945-957. doi: 10.1007/s12033-019-00217-y. Mol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31664705
-
Knowns and unknowns of TiLV-associated neuronal disease.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2329568. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2329568. Epub 2024 Mar 31. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38555518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of In Silico Approaches for Discovering Natural Viral Protein Inhibitors in Aquaculture Disease Control.J Fish Dis. 2025 Jul;48(7):e14120. doi: 10.1111/jfd.14120. Epub 2025 Mar 20. J Fish Dis. 2025. PMID: 40111154 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying therapeutic target for prostate cancer: exploring Diosmetin as a CYP inhibitor.Discov Oncol. 2024 Dec 20;15(1):814. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01711-9. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39704776 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Antibacterial Potential of Artemisia judaica Compounds Targeting the Hydrolase/Antibiotic Protein in Klebsiella pneumoniae: In Vitro and In Silico Investigations.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 22;17(6):667. doi: 10.3390/ph17060667. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931335 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput screening of natural antiviral drug candidates against white spot syndrome virus targeting VP28 in Penaeus monodon: Computational drug design approaches.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2025 Mar;23(1):100455. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2024.100455. Epub 2024 Dec 28. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40074429 Free PMC article.
-
Green tea extract reduces viral proliferation and ROS production during Feline Herpesvirus type-1 (FHV-1) infection.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Aug 22;20(1):374. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04227-0. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39175036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saranya SR, Sudhakaran R. Report on prevalence of tilapia lake virus infection in tilapia fishes (Oreochromis niloticus). Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2020;27: 101665. doi: 10.1016/J.BCAB.2020.101665 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

