Targeting the TCA cycle through cuproptosis confers synthetic lethality on ARID1A-deficient hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37939712
- PMCID: PMC10694624
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101264
Targeting the TCA cycle through cuproptosis confers synthetic lethality on ARID1A-deficient hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
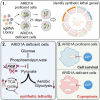
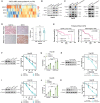
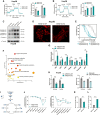
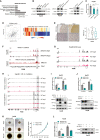
ARID1A is among the most commonly mutated tumor suppressor genes in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this study, we conduct a CRISPR-Cas9 synthetic lethality screen using ARID1A-deficient HCC cells to identify approaches to treat HCC patients harboring ARID1A deficiency. This strategy reveals that the survival of these ARID1A-deficient HCC cells is highly dependent on genes related to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Mechanistically, ARID1A loss represses expression of key glycolysis-related gene PKM, shifting cellular glucose metabolism from aerobic glycolysis to dependence on the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Cuproptosis is a recently defined form of copper-induced cell death reported to directly target the TCA cycle. Here, we find that ARID1A-deficient HCC cells and xenograft tumors are highly sensitive to copper treatment. Together, these results offer evidence of the synthetic lethality between ARID1A deficiency and mitochondrial respiration impairment, suggesting that copper treatment constitutes a promising therapeutic strategy for selectively targeting ARID1A-deficient HCC.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests All the authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting USP9X-AMPK Axis in ARID1A-Deficient Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;14(1):101-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2022.03.009. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35390516 Free PMC article.
-
Arid1a regulates response to anti-angiogenic therapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2018 Mar;68(3):465-475. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.10.028. Epub 2017 Nov 4. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29113912
-
BRD4 inhibition induces synthetic lethality in ARID2-deficient hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing DNA damage.Oncogene. 2022 Mar;41(10):1397-1409. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02176-2. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35017665
-
Molecular and pathological landscape of the AT-rich interaction domain 1A (ARID1A) mutation in hepatocellular carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2025 Feb;266:155763. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155763. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Pathol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 39706068 Review.
-
Treating ARID1A mutated cancers by harnessing synthetic lethality and DNA damage response.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Sep 19;29(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00856-5. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 36123603 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PLOD1 promotes the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma by facilitating the NF-κB/IL-6/STAT3-dependent TCA cycle.JHEP Rep. 2025 Jan 20;7(5):101329. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2025.101329. eCollection 2025 May. JHEP Rep. 2025. PMID: 40290518 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Alanine Transporter Utilization is a Therapeutic Vulnerability in ARID1A-Mutant Ovarian Cancer.Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 14:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-25-0654. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-25-0654. Online ahead of print. Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40658600 Free PMC article.
-
Cuproplasia and cuproptosis, two sides of the coin.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2025 May;45(5):505-524. doi: 10.1002/cac2.70001. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39865459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Arachidonic Acid Metabolism Enhances Immunotherapy Efficacy in ARID1A-Deficient Colorectal Cancer.Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 3;85(5):925-941. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-1611. Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39652583 Free PMC article.
-
Sex disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy: hormonal and genetic influences on treatment efficacy.Front Immunol. 2025 May 14;16:1607374. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1607374. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40438106 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hilmi M., Neuzillet C., Calderaro J., Lafdil F., Pawlotsky J.M., Rousseau B. Angiogenesis and immune checkpoint inhibitors as therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: current knowledge and future research directions. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2019;7:333. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0824-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guichard C., Amaddeo G., Imbeaud S., Ladeiro Y., Pelletier L., Maad I.B., Calderaro J., Bioulac-Sage P., Letexier M., Degos F., et al. Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and focal copy-number changes identifies key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012;44:694–698. doi: 10.1038/ng.2256. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

