Macrophage phenotypes and functions: resolving inflammation and restoring homeostasis
- PMID: 37940394
- PMCID: PMC10841626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2023.10.004
Macrophage phenotypes and functions: resolving inflammation and restoring homeostasis
Abstract
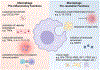
Inflammation must be tightly regulated to both defend against pathogens and restore tissue homeostasis. The resolution of inflammatory responses is a dynamic process orchestrated by cells of the immune system. Macrophages, tissue-resident innate immune cells, are key players in modulating inflammation. Here, we review recent work highlighting the importance of macrophages in tissue resolution and the return to homeostasis. We propose that enhancing macrophage pro-resolution functions represents a novel and widely applicable therapeutic strategy to dampen inflammation, promote repair, and restore tissue integrity and function.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; efferocytosis; fibrosis; inflammation; macrophages; tissue repair.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests No interests are declared.
Figures

References
-
- Okabe Y and Medzhitov R (2016) Tissue biology perspective on macrophages. Nat. Immunol 17, 9–17 - PubMed
-
- Jenkins SJ and Allen JE (2021) The expanding world of tissue-resident macrophages. Eur. J. Immunol 51, 1882–1896 - PubMed
-
- Franklin RA (2021) Fibroblasts and macrophages: Collaborators in tissue homeostasis. Immunol. Rev 302, 86–103 - PubMed
-
- Meizlish ML et al. (2021) Tissue Homeostasis and Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Immunol 39, 1–25 - PubMed
-
- Choutka J. et al. (2022) Unexplained post-acute infection syndromes. Nat. Med 28, 911–923 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

