Detection of Wuchereria bancrofti in human blood samples and mosquitoes in Matayos, Busia County-Kenya
- PMID: 37940673
- PMCID: PMC10632445
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-46329-z
Detection of Wuchereria bancrofti in human blood samples and mosquitoes in Matayos, Busia County-Kenya
Abstract
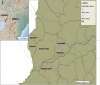
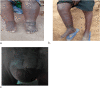
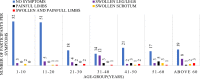
Lymphatic filariasis is a mosquito borne disease which leads to abnormal painful enlarged body parts, severe disability and social stigma. We screened Wuchereria bancrofti in Matayos constituency in Busia County. Blood samples were collected from 23 villages selected purposively based on clinical case reports. Finger prick and/or venous blood sampling and mosquito collections was carried out. Antigenaemia and filarial DNA prevalence were determined. Infection rates on mosquito pools were estimated and SPSS version 26 was used for descriptive statistics analysis. A total of 262 participants were recruited, 73.3% (n = 192) of the participants had no symptoms, 14.1% (n = 5.3) had swollen legs, 5.3% (n = 14) had painful legs and 3.8% (n = 10) with scrotal swellings. Average antigenemia prevalence was 35.9% (n = 94) and DNA prevalence was at 8.0% (n = 21). A total of 1305 mosquitoes were collected and pooled into 2-20 mosquitoes of the same species and from the same village. Two pools out of 78 were positive for filarial DNA with a minimum infection rate of 0.15%. From this study, antigenaemia and infected mosquitoes are an indication of active transmission. The clinical signs are evidence that filarial infections have been in circulation for over 10 years. The global climate change phenomenon currently happening has been shown to adversely affect the transmission of vector borne diseases and is likely to increase lymphatic filariasis transmission in the area. This study therefore recommends further screening before Mass Drug Administration, morbidity management and enhanced mosquito control Programmes are recommended in the study area.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. Validation of Elimination of Lymphatic Filariasis as a Public Health Problem. Geneva. http://WHO/HTM/NTD/PCT/2017.01 (2017).
-
- Okulewicz A. The impact of global climate change on the spread of parasitic nematodes. Ann. Parasitol. 2017;63(1):15–20. - PubMed
-
- Hemalatha KVRP. Impact of lymphatic filariasis on quality of life of affected individuals: A community based cross sectional survey. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2016;6:13–18.
-
- Martindale, S., Mkwanda, S.Z., Smith, E., Molyneux, D., Stanton, M.C. & Kelly-Hope, L.A. Quantifying the physical and socio-economic burden of filarial lymphoedema in Chikwawa District, Malawi. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg.108(12), 759–67 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

