Decision regret among couples experiencing infertility: a mixed methods longitudinal cohort study
- PMID: 37940984
- PMCID: PMC10633954
- DOI: 10.1186/s12978-023-01699-5
Decision regret among couples experiencing infertility: a mixed methods longitudinal cohort study
Abstract
Background: Decisions for how to resolve infertility are complex and may lead to regret. We examined whether couples and individuals who sought a consultation from a reproductive specialist for infertility later expressed decisional regret about their family-building choices and whether regret was associated with parental role, family-building paths, or outcomes.
Methods: This longitudinal mixed methods study included women and their partners who completed a questionnaire prior to their initial consultation with a reproductive specialist and 6 years later. The six-year questionnaire included the Ottawa Decision Regret Scale referencing "the decisions you made about how to add a child to your family." A score of 25+ indicates moderate-to-severe regret. Additional items invited reflections on family-building decisions, treatments, and costs. A systematic content analysis assessed qualitative themes.
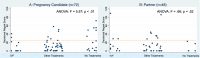
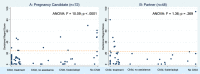
Results: Forty-five couples and 34 individuals participated in the six-year questionnaire (76% retention rate), Half (n = 61) of participants expressed no regret, which was similar by role (median 0 for women and supporting partners, F = .08; p = .77). One in 5 women and 1 in 7 partners expressed moderate-to-severe regret. Women who did not pursue any treatment had significantly higher regret (median 15; F = 5.6, p < 0.01) compared to those who pursued IVF (median 0) or other treatments (median 0). Women who did not add a child to their family had significantly higher regret (median 35; F = 10.1, p < 0.001) than those who added a child through treatment (median 0), through fostering/adoption (median 0), or naturally (median 5). Among partners, regret scores were not associated with family-building paths or outcomes. More than one-quarter of participants wished they had spent less money trying to add a child to their family. Qualitative themes included gratitude for parenthood despite the burdensome process of family-building as well as dissatisfaction or regret about the process. Results should be confirmed in other settings to increase generalizability.
Conclusion: This longitudinal study provides new insight into the burden of infertility. For women seeking parenthood, any of the multiple paths to parenthood may prevent future decision regret. Greater psychosocial, financial, and decision support is needed to help patients and their partners navigate family-building with minimal regret.
Keywords: Decision regret; Decision-making; Decisional regret scale; Fertility treatment; Infertility; Mixed methods.
Plain language summary
When people experience infertility, there are many decisions that can be challenging, such as whether to seek fertility treatments, to pursue fostering/adoption, and how to manage costs. With each decision, there is an opportunity for regret. The goal of this study was to look at whether people who were experiencing infertility and made an appointment with a doctor who specializes in infertility felt any regret about their decisions 6 years later. We also looked at whether different roles (that is, women seeking pregnancy or their supporting partners), different family-building paths (that is, medical treatments or not), or different outcomes (that is, adding a child to their family or not) were associated with different levels of regret. Results showed that half of the 120 people in the study did not have any regret 6 years after meeting with a specialty doctor. However, some patients did have regret, including 20% of women and 14% of partners who expressed moderate-to-severe regret. Women who did not add a child to their family in the six years during the study reported higher regret compared to women who did add a child to their family. There were no such differences among partners. About 25% of participants wished they had tried more, fewer, or different treatments. More than 25% wished they spent less money to try to add a child to their family. For people who want to add a child to their family, there are multiple ways to become a parent, any of which may be linked to lower decision regret. Decision regret is experienced differently between women seeking to add a child to their family and their partners. Would-be parents need more emotional, financial, and decision making support to help them navigate family-building with minimal regret.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Rachel Cusatis—None. Colin Johnson—None. Kate Schoyer—None. Shirng-Wern Tsaih—None. Joanna Balza—None. Jay Sandlow—None. Kathryn Flynn—None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decisional conflict among couples seeking specialty treatment for infertility in the USA: a longitudinal exploratory study.Hum Reprod. 2020 Mar 27;35(3):573-582. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dez292. Hum Reprod. 2020. PMID: 32154565 Free PMC article.
-
Priorities for family building among patients and partners seeking treatment for infertility.Reprod Health. 2017 Apr 5;14(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12978-017-0311-8. Reprod Health. 2017. PMID: 28381306 Free PMC article.
-
Permanently infertile couples and family building-a cross-sectional survey in Denmark.Hum Reprod. 2024 Nov 1;39(11):2525-2536. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deae208. Hum Reprod. 2024. PMID: 39272230 Free PMC article.
-
Infertility and assisted reproduction in Denmark. Epidemiology and psychosocial consequences.Dan Med Bull. 2006 Nov;53(4):390-417. Dan Med Bull. 2006. PMID: 17150146 Review.
-
Driving factors in treatment decision-making of patients seeking medical assistance for infertility: a systematic review.Hum Reprod Update. 2024 May 2;30(3):341-354. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmae001. Hum Reprod Update. 2024. PMID: 38305635 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Health care experiences of individuals accessing or undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) in the U.S.: a narrative review of qualitative studies.Front Reprod Health. 2025 Feb 13;7:1490917. doi: 10.3389/frph.2025.1490917. eCollection 2025. Front Reprod Health. 2025. PMID: 40017896 Free PMC article.
-
Postpartum Sterilization after a Preterm Delivery Is Not Associated with Decision Regret.Med Decis Making. 2025 Aug;45(6):654-664. doi: 10.1177/0272989X251341478. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Med Decis Making. 2025. PMID: 40542624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zegers-Hochschild F, Adamson GD, De Mouzon J, Ishihara O, Mansour R, Nygren K, et al. The International Committee for Monitoring Assisted Reproductive Technology (ICMART) and the World Health Organization (WHO) revised glossary on ART terminology, 2009. Hum Reprod. 2009;24(11):2683–2687. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dep343. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical