AMPK activator-treated human cardiac spheres enhance maturation and enable pathological modeling
- PMID: 37941041
- PMCID: PMC10633979
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-023-03554-7
AMPK activator-treated human cardiac spheres enhance maturation and enable pathological modeling
Abstract
Background: Cardiac pathological outcome of metabolic remodeling is difficult to model using cardiomyocytes derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC-CMs) due to low metabolic maturation.
Methods: hiPSC-CM spheres were treated with AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activators and examined for hiPSC-CM maturation features, molecular changes and the response to pathological stimuli.
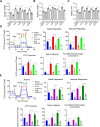
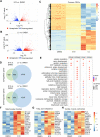
Results: Treatment of hiPSC-CMs with AMPK activators increased ATP content, mitochondrial membrane potential and content, mitochondrial DNA, mitochondrial function and fatty acid uptake, indicating increased metabolic maturation. Conversely, the knockdown of AMPK inhibited mitochondrial maturation of hiPSC-CMs. In addition, AMPK activator-treated hiPSC-CMs had improved structural development and functional features-including enhanced Ca2+ transient kinetics and increased contraction. Transcriptomic, proteomic and metabolomic profiling identified differential levels of expression of genes, proteins and metabolites associated with a molecular signature of mature cardiomyocytes in AMPK activator-treated hiPSC-CMs. In response to pathological stimuli, AMPK activator-treated hiPSC-CMs had increased glycolysis, and other pathological outcomes compared to untreated cells.
Conclusion: AMPK activator-treated cardiac spheres could serve as a valuable model to gain novel insights into cardiac diseases.
Keywords: AMPK; Cardiomyocytes; Maturation; Metabolic regulation; Pathological modeling; Stem cells.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Gentillon C, Li D, Duan M, Yu WM, Preininger MK, Jha R, Rampoldi A, Saraf A, Gibson GC, Qu CK, Brown LA, Xu C. Targeting HIF-1alpha in combination with PPARalpha activation and postnatal factors promotes the metabolic maturation of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;132:120–135. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.05.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu D, Linders A, Yamak A, Correia C, Kijlstra JD, Garakani A, Xiao L, Milan DJ, van der Meer P, Serra M, Alves PM, Domian IJ. Metabolic maturation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes by inhibition of HIF1alpha and LDHA. Circ Res. 2018;123(9):1066–1079. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313249. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

