A review on factors related to patient comfort experience in hospitals
- PMID: 37941052
- PMCID: PMC10634154
- DOI: 10.1186/s41043-023-00465-4
A review on factors related to patient comfort experience in hospitals
Abstract
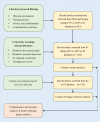
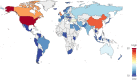
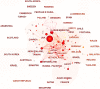
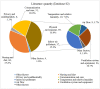
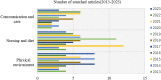
The creation of a welcoming hospital atmosphere is necessary to improve patient wellbeing and encourage healing. The goal of this study was to examine the variables affecting hospitalised patients' comfort. The study procedure included a thorough search of the Web of Science and Scopus databases, as well as the use of software analytic tools to graphically map enormous literature data, providing a deeper understanding of the linkages within the literature and its changing patterns. Insights from a range of disciplines, including engineering, psychology, immunology, microbiology, and environmental science, were included into our study using content analysis and clustering approaches. The physical environment and the social environment are two crucial factors that are related to patient comfort. The study stress the need of giving patient comfort a top priority as they heal, especially by tackling indoor air pollution. Our research also emphasises how important hospital care and food guidelines are for improving patient comfort. Prioritising patients who need specialised care and attention, especially those who have suffered trauma, should be the focus of future study. Future research in important fields including trauma, communication, hospital architecture, and nursing will be built on the findings of this study. To enhance research in these crucial areas, worldwide collaboration between experts from other nations is also advised. Although many studies stress the significance of patient comfort, few have drawn conclusions from a variety of disciplines, including medicine, engineering, immunology, microbiology, and environmental science, the most crucial issue of thoroughly researching the improvement of patient comfort has not been addressed. Healthcare workers, engineers, and other professions will benefit greatly from this study's investigation of the connection between hospital indoor environments and patient comfort.
Keywords: Air purification; Hospital environment; Indoor air quality; Physical environment; Thermal comfort.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Asmarawati TP, Arfijanto MV, Hadi U, Miftahussurur M. Healthcare associated covid-19 transmission: strategies to prevent. New Armenian Med J. 2020;14(4):29–36.
-
- Horve PF, Lloyd S, Mhuireach GA, Dietz L, Fretz M, MacCrone G, Van den Wymelenberg K, Ishaq SL. Building upon current knowledge and techniques of indoor microbiology to construct the next era of theory into microorganisms, health, and the built environment. J Exposure Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2020;30(2):219–235. doi: 10.1038/s41370-019-0157-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yeo LB. Psychological and physiological benefits of plants in the indoor environment: a mini and in-depth review. Int J Built Environ Sustain. 2021;8(1):57–67. doi: 10.11113/ijbes.v8.n1.597. - DOI
-
- McCormack MC, Belli AJ, Waugh D, Matsui EC, Peng RD, Williams DAL, Paulin L, Saha A, Aloe CM, Diette GB, Breysse PN, Hansel NN. Respiratory effects of indoor heat and the interaction with air pollution in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016;13(12):2125–2131. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201605-329OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tacutu L, Nastase I, Catalina T. A critical regard on Romanian regulations related to Indoor Environment Quality in Operating Rooms and a technical case study. In: Conference on sustainable solutions for energy and environment (EENVIRO - YRC). 2015. Bucharest, Romania
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

