Central pontine myelinolysis: a rare finding in hyperosmolar hyperglycemia
- PMID: 37941579
- PMCID: PMC10628315
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1216328
Central pontine myelinolysis: a rare finding in hyperosmolar hyperglycemia
Abstract
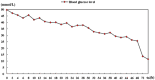
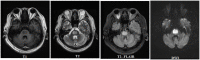
Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) is a heterogeneous nervous system disease of pontine demyelination, usually caused by rapid correction of hyponatremia. In the present study, we report a unique case of a 46-year-old man with a hyperglycemic state complicated with CPM. MRI demonstrated a high signal on T2 and symmetric restricted diffusion in the pontine. In conclusion, the clinical case described confirmed that the hyperosmolar state inherent in hyperglycemia was a likely cause of CPM.
Keywords: blood glucose; central pontine myelinolysis; hyperosmolar; hyponatremia; osmotic demyelination syndrome.
Copyright © 2023 Qu, Sun and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rodríguez-Velver KV, Soto-Garcia AJ, Zapata-Rivera MA, Montes-Villarreal J, Villarreal-Pérez JZ, Rodríguez-Gutiérrez R. Osmotic demyelination syndrome as the initial manifestation of a hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Case Rep Neurol Med. (2014) 2014:652523. doi: 10.1155/2014/652523, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources