Extracellular vesicles hybrid plasmid-loaded lipid nanovesicles for synergistic cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 37942423
- PMCID: PMC10628780
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100845
Extracellular vesicles hybrid plasmid-loaded lipid nanovesicles for synergistic cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
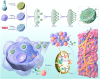
Combination immunotherapy of cancer vaccines with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) represents a promising therapeutic strategy for immunosuppressed and cold tumors. However, this strategy still faces challenges, including the limited therapeutic efficacy of cancer vaccines and immune-related adverse events associated with systematic delivery of ICIs. Herein, we demonstrate the antitumor immune response induced by outer membrane vesicle from Akkermansia muciniphila (Akk-OMV), which exhibites a favorable safety profile, highlighting the potential application as a natural and biocompatible self-adjuvanting vesicle. Utilizing tumor cell-derived exosome as an antigen source and Akk-OMV as a natural adjuvant, we construct a cancer vaccine formulation of extracellular vesicles hybrid lipid nanovesicles (Lipo@HEV) for enhanced prophylactic and therapeutic vaccination by promoting dendritic cell (DC) maturation in lymph node and activating cytotoxic T cell (CTL) response. The Lipo@HEV is further loaded with plasmid to enable gene therapy-mediated PD-L1 blockade upon peritumoral injection. Meanwhile, it penetrates into lymph node to initiate DC maturation and CTL activation, synergistically inhibiting the established tumor. The fabrication of extracellular vesicles hybrid plasmid-loaded lipid nanovesicles reveals a promising gene therapy-guided and vesicle-based hybrid system for therapeutic cancer vaccination and synergistic immunotherapy strategy.
Keywords: Akkermansia muciniphila; Cancer vaccine; Extracellular vesicles; Hybrid lipid nanovesicles; Immune checkpoint blockade; Liposomes.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Xiaoyuan Huang reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100001809National Natural Science Foundation of China and 10.13039/501100003819Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province.
Figures




References
-
- Saxena M., van der Burg S.H., Melief C.J.M., Bhardwaj N. Therapeutic cancer vaccines. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2021;21:360–378. - PubMed
-
- Lin M.J., Svensson-Arvelund J., Lubitz G.S., Marabelle A., Melero I., Brown B.D., Brody J.D. Cancer vaccines: the next immunotherapy frontier. Nat. Can. (Ott.) 2022;3:911–926. - PubMed
-
- Ye T., Li F., Ma G., Wei W. Enhancing therapeutic performance of personalized cancer vaccine via delivery vectors. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021;177 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

