Effect of Swine Glyco-humanized Polyclonal Neutralizing Antibody on Survival and Respiratory Failure in Patients Hospitalized With Severe COVID-19: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- PMID: 37942459
- PMCID: PMC10629360
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofad525
Effect of Swine Glyco-humanized Polyclonal Neutralizing Antibody on Survival and Respiratory Failure in Patients Hospitalized With Severe COVID-19: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: We evaluated the safety and efficacy of XAV-19, an antispike glyco-humanized swine polyclonal neutralizing antibody in patients hospitalized with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Methods: This phase 2b clinical trial enrolled adult patients from 34 hospitals in France. Eligible patients had a confirmed diagnosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 within 14 days of onset of symptoms that required hospitalization for low-flow oxygen therapy (<6 L/min of oxygen). Patients were randomly assigned to receive a single intravenous infusion of 2 mg/kg of XAV-19 or placebo. The primary end point was the occurrence of death or severe respiratory failure between baseline and day 15.
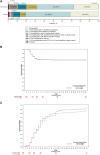
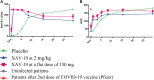
Results: Between January 12, 2021, and April 16, 2021, 398 patients were enrolled in the study and randomly assigned to XAV-19 or placebo. The modified intention-to-treat population comprised 388 participants who received full perfusion of XAV-19 (199 patients) or placebo (189 patients). The mean (SD) age was 59.8 (12.4) years, 249 (64.2%) individuals were men, and the median time (interquartile range) from symptom onset to enrollment was 9 (7-10) days. There was no statistically significant decrease in the cumulative incidence of death or severe respiratory failure through day 15 in the XAV-19 group vs the placebo group (53/199 [26.6%] vs 48/189 [25.4%]; adjusted risk difference, 0.6%; 95% CI, -6% to 7%; hazard ratio, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.64-1.66; P = .90). In the safety population, adverse events were reported in 75.4% of 199 patients in the XAV-19 group and in 76.3% of 190 patients in the placebo group through D29.
Conclusions: Among patients hospitalized with COVID-19 requiring low-flow oxygen therapy, treatment with a single intravenous dose of XAV-19, compared with placebo, did not show a significant difference in terms of disease progression at day 15.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; XAV-19; clinical trial; polyclonal glyco-humanized anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. B.G. reports receipt of nonfinancial support from Gilead Sciences and MSD, outside the submitted work. B.V. is an employee and chief scientific officer/operating officer of Xenothera and owns shares and holds share options in Xenothera. K.L. reports receipt of personal fees and nonfinancial support from AbbVie, Chiesi, Healthcare, Janssen, MSD, and ViiV, outside the submitted work. V.D. reports receipt of nonfinancial support from Gilead Sciences, MSD, and Sanofi-Pasteur, outside the submitted work. O.D. is a cofounder of Xenothera, is the CEO of Xenothera, and owns shares and holds share options in Xenothera. F.R. reports receipt of personal fees from AbbVie, Astra Zeneca, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck, Roche, ViiV Healthcare, and Xenothera, outside the submitted work. L.P. owns shares in Novartis. All other authors report no potential conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020; 323:1239–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

