HNF1α maintains pancreatic α and β cell functions in primary human islets
- PMID: 37943614
- PMCID: PMC10807710
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.170884
HNF1α maintains pancreatic α and β cell functions in primary human islets
Abstract
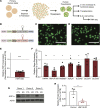
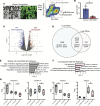
HNF1A haploinsufficiency underlies the most common form of human monogenic diabetes (HNF1A-maturity onset diabetes of the young [HNF1A-MODY]), and hypomorphic HNF1A variants confer type 2 diabetes risk. But a lack of experimental systems for interrogating mature human islets has limited our understanding of how the transcription factor HNF1α regulates adult islet function. Here, we combined conditional genetic targeting in human islet cells, RNA-Seq, chromatin mapping with cleavage under targets and release using nuclease (CUT&RUN), and transplantation-based assays to determine HNF1α-regulated mechanisms in adult human pancreatic α and β cells. Short hairpin RNA-mediated (shRNA-mediated) suppression of HNF1A in primary human pseudoislets led to blunted insulin output and dysregulated glucagon secretion after transplantation in mice, recapitulating phenotypes observed in patients with diabetes. These deficits corresponded with altered expression of genes encoding factors critical for hormone secretion, including calcium channel subunits, ATPase transporters, and extracellular matrix constituents. Additionally, HNF1A loss led to upregulation of transcriptional repressors, providing evidence for a mechanism of transcriptional derepression through HNF1α. CUT&RUN mapping of HNF1α DNA binding sites in primary human islets imputed a subset of HNF1α-regulated genes as direct targets. These data elucidate mechanistic links between HNF1A loss and diabetic phenotypes in mature human α and β cells.
Keywords: Beta cells; Diabetes; Endocrinology; Genetics; Monogenic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
HNF1α controls glucagon secretion in pancreatic α-cells through modulation of SGLT1.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Nov 1;1866(11):165898. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165898. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020. PMID: 32711050 Free PMC article.
-
Hnf1alpha (MODY3) controls tissue-specific transcriptional programs and exerts opposed effects on cell growth in pancreatic islets and liver.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Jun;29(11):2945-59. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01389-08. Epub 2009 Mar 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19289501 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of HNF1α and HNF4α in pancreatic β-cells: lessons from a monogenic form of diabetes (MODY).Vitam Horm. 2014;95:407-23. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800174-5.00016-8. Vitam Horm. 2014. PMID: 24559927 Review.
-
Tubular proteinuria in patients with HNF1α mutations: HNF1α drives endocytosis in the proximal tubule.Kidney Int. 2016 May;89(5):1075-1089. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.01.027. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 27083284
-
HNF1A:From Monogenic Diabetes to Type 2 Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 1;13:829565. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.829565. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35299962 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting β-Cell Plasticity: A Promising Approach for Diabetes Treatment.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 18;46(7):7621-7667. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070453. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating Mendelian randomization and single-cell RNA sequencing to identify therapeutic targets of baicalin for type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 26;15:1403943. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1403943. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39130628 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Roles of Common Genetic Variants and Their Contributions to Diabetes: MODY and Uncontrolled T2DM.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 14;15(3):414. doi: 10.3390/biom15030414. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 OD025212/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK107507/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK108817/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK098085/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK128932/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK138492/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD021763/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007790/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK126482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK123743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK116074/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

