MACE and VTE across upadacitinib clinical trial programmes in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis
- PMID: 37945286
- PMCID: PMC10649869
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003392
MACE and VTE across upadacitinib clinical trial programmes in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis
Abstract
Objectives: To provide an integrated analysis of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) and events of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and associated risk factors across rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) phase 2b/3 upadacitinib clinical programmes.
Methods: Data were analysed and summarised from clinical trials of RA, PsA and AS treated with upadacitinib 15 mg once daily (QD) and 30 mg QD (as of 30 June 2021). Data from adalimumab (RA and PsA) and methotrexate (RA) arms were included as comparators. Adjudicated MACEs and VTE events were presented as exposure-adjusted rates per 100 patient-years (E/100 PY). Univariable Cox proportional hazard regression analyses assessed potential associations of risk factors for MACE and VTE.
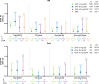
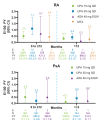
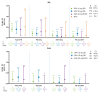
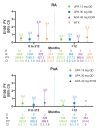
Results: In total, 4298 patients received upadacitinib 15 mg (RA n=3209, PsA n=907 and AS n=182) and 2125 patients received upadacitinib 30 mg (RA n=1204 and PsA n=921). In patients with RA and PsA, rates of MACE (0.3-0.6 E/100 PY) and VTE (0.2-0.4 E/100 PY) were similar across upadacitinib doses; in patients with AS, no MACEs and one VTE event occurred. Most patients experiencing MACEs or VTE events had two or more baseline cardiovascular risk factors. Across RA and PsA groups, rates of MACEs and VTE events were similar.
Conclusions: Rates of MACEs and VTE events with upadacitinib were consistent with previously reported data for patients receiving conventional synthetic and biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and comparable with active comparators adalimumab and methotrexate. Associated patient characteristics are known risk factors for MACEs and VTE events.
Trial registration numbers: RA (SELECT-NEXT: NCT02675426; SELECT-MONOTHERAPY: NCT02706951; SELECT-BEYOND: NCT02706847; SELECT-COMPARE: NCT02629159; SELECT-EARLY: NCT02706873, SELECT-CHOICE: NCT03086343), PsA (SELECT-PsA 2: NCT03104374; SELECT-PsA 1: NCT03104400), and AS (SELECT-AXIS 1: NCT03178487).
Keywords: Antirheumatic Agents; Arthritis, Psoriatic; Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Spondylitis, Ankylosing.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CC-S has received grant/research support from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CSL Behring, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Priovant Therapeutics and Pfizer. She is a consultant for AbbVie, Priovant Therapeutics, Octapharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, Galapagos and Sanofi-Regeneron. EC has received research grants and/or has served as member of advisory boards and/or speaker bureaus for AbbVie, Amgen, Bio-Cancer, Biocon, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Chugai Pharma, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, Gilead, Inmedix, Janssen, Merck Serono, Novimmune, Novartis, ObsEva, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, R-Pharm, Sanofi, SynAct Pharma and UCB. IBM has received research grants and/or consulting fees from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, EveloBio, Janssen, LEO, Lilly, Novartis, Moonlake, Pfizer and UCB. EM has received research grants and/or has served as a member of advisory boards and/or speaker bureaus for AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, BMS, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Sandoz and Roche. PN has received research grants and/or consulting fees from and/or is a member of speakers’ bureaus for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead and Janssen. KY is a member of speakers’ bureaus for AbbVie, GK, Astellas, BMS, Chugai, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Pfizer and Takeda. RL, NK, HP, AKS and JS are full-time employees of AbbVie and may hold AbbVie stock or stock options. JRC has received research grants and/or consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, ArthritisPower, Aqtual, Bendcare, BMS, CorEvitas, FASTER, GSK, IlluminationHealth, Janssen, Labcorp, Lilly, Myriad, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Scipher, Setpoint and UCB.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
