International Guideline for Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy-Associated Cancer Screening: an International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group (IMACS) initiative
- PMID: 37945774
- PMCID: PMC10834225
- DOI: 10.1038/s41584-023-01045-w
International Guideline for Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy-Associated Cancer Screening: an International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group (IMACS) initiative
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: International Guideline for Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy-Associated Cancer Screening: an International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group (IMACS) initiative.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024 May;20(5):315. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01111-x. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38548933 No abstract available.
Abstract
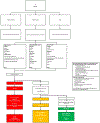
Adult-onset idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) is associated with an increased cancer risk within the 3 years preceding and following IIM onset. Evidence- and consensus-based recommendations for IIM-associated cancer screening can potentially improve outcomes. This International Guideline for IIM-Associated Cancer Screening provides recommendations addressing IIM-associated cancer risk stratification, cancer screening modalities and screening frequency. The international Expert Group formed a total of 18 recommendations via a modified Delphi approach using a series of online surveys. First, the recommendations enable an individual patient's IIM-associated cancer risk to be stratified into standard, moderate or high risk according to the IIM subtype, autoantibody status and clinical features. Second, the recommendations outline a 'basic' screening panel (including chest radiography and preliminary laboratory tests) and an 'enhanced' screening panel (including CT and tumour markers). Third, the recommendations advise on the timing and frequency of screening via basic and enhanced panels, according to risk status. The recommendations also advise consideration of upper or lower gastrointestinal endoscopy, nasoendoscopy and 18F-FDG PET-CT scanning in specific patient populations. These recommendations are aimed at facilitating earlier IIM-associated cancer detection, especially in those who are at a high risk, thus potentially improving outcomes, including survival.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Figures
References
-
- Chinoy H & Cooper RG Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. in Oxford Textbook of Rheumatology 1009–1020 (Oxford University Press, 2013). doi:10.1093/med/9780199642489.003.0124_update_001 - DOI
-
- Qiang JK, Kim WB, Baibergenova A & Alhusayen R Risk of malignancy in dermatomyositis and polymyositis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cutan. Med. Surg 21, 131–136 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Dobloug GC, Garen T, Brunborg C, Gran JT & Molberg Ø Survival and cancer risk in an unselected and complete Norwegian idiopathic inflammatory myopathy cohort. Semin. Arthritis Rheum 45, 301–308 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Kang EH et al. Temporal relationship between cancer and myositis identifies two distinctive subgroups of cancers: impact on cancer risk and survival in patients with myositis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 55, 1631–41 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

