Non-synaptic function of the autism spectrum disorder-associated gene SYNGAP1 in cortical neurogenesis
- PMID: 37946050
- PMCID: PMC11349286
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01477-3
Non-synaptic function of the autism spectrum disorder-associated gene SYNGAP1 in cortical neurogenesis
Abstract
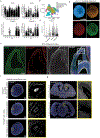
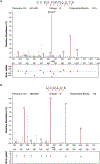
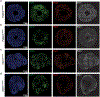
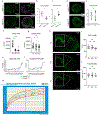
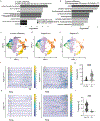
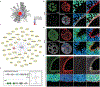
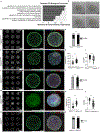
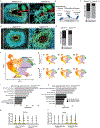
Genes involved in synaptic function are enriched among those with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)-associated rare genetic variants. Dysregulated cortical neurogenesis has been implicated as a convergent mechanism in ASD pathophysiology, yet it remains unknown how 'synaptic' ASD risk genes contribute to these phenotypes, which arise before synaptogenesis. Here, we show that the synaptic Ras GTPase-activating (RASGAP) protein 1 (SYNGAP1, a top ASD risk gene) is expressed within the apical domain of human radial glia cells (hRGCs). In a human cortical organoid model of SYNGAP1 haploinsufficiency, we find dysregulated cytoskeletal dynamics that impair the scaffolding and division plane of hRGCs, resulting in disrupted lamination and accelerated maturation of cortical projection neurons. Additionally, we confirmed an imbalance in the ratio of progenitors to neurons in a mouse model of Syngap1 haploinsufficiency. Thus, SYNGAP1-related brain disorders may arise through non-synaptic mechanisms, highlighting the need to study genes associated with neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) in diverse human cell types and developmental stages.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Jourdon A. et al. ASD modelling in organoids reveals imbalance of excitatory cortical neuron subtypes during early neurogenesis. bioRxiv, 2022.2003.2019.484988 (2022). 10.1101/2022.03.19.484988 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

