Near-Infrared-Responsive Rare Earth Nanoparticles for Optical Imaging and Wireless Phototherapy
- PMID: 37946706
- PMCID: PMC10885668
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202305308
Near-Infrared-Responsive Rare Earth Nanoparticles for Optical Imaging and Wireless Phototherapy
Abstract
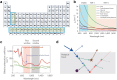
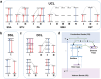
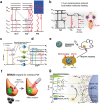
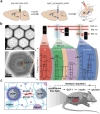
Near-infrared (NIR) light is well-suited for the optical imaging and wireless phototherapy of malignant diseases because of its deep tissue penetration, low autofluorescence, weak tissue scattering, and non-invasiveness. Rare earth nanoparticles (RENPs) are promising NIR-responsive materials, owing to their excellent physical and chemical properties. The 4f electron subshell of lanthanides, the main group of rare earth elements, has rich energy-level structures. This facilitates broad-spectrum light-to-light conversion and the conversion of light to other forms of energy, such as thermal and chemical energies. In addition, the abundant loadable and modifiable sites on the surface offer favorable conditions for the functional expansion of RENPs. In this review, the authors systematically discuss the main processes and mechanisms underlying the response of RENPs to NIR light and summarize recent advances in their applications in optical imaging, photothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy, photoimmunotherapy, optogenetics, and light-responsive drug release. Finally, the challenges and opportunities for the application of RENPs in optical imaging and wireless phototherapy under NIR activation are considered.
Keywords: near-infrared light; optical imaging; photoconversion; phototherapy; rare earth nanoparticles.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Light Conversion Nanomaterials for Wireless Phototherapy.Acc Chem Res. 2023 May 16;56(10):1143-1155. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00699. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Acc Chem Res. 2023. PMID: 36897248
-
Enhanced photoconversion performance of NdVO4/Au nanocrystals for photothermal/photoacoustic imaging guided and near infrared light-triggered anticancer phototherapy.Acta Biomater. 2019 Nov;99:295-306. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.08.026. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31437636
-
Tumor-targeted and multi-stimuli responsive drug delivery system for near-infrared light induced chemo-phototherapy and photoacoustic tomography.Acta Biomater. 2016 Jul 1;38:129-42. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.04.024. Epub 2016 Apr 16. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 27090593
-
NIR-II phototherapy agents with aggregation-induced emission characteristics for tumor imaging and therapy.Biomaterials. 2022 Jun;285:121535. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121535. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Biomaterials. 2022. PMID: 35487066 Review.
-
Near-IR responsive nanostructures for nanobiophotonics: emerging impacts on nanomedicine.Nanomedicine. 2016 Apr;12(3):771-788. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2015.11.009. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 26656629 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-time detection and resection of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer through a rare earth nanoprobe based NIR-IIb fluorescence imaging.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Jul 30;28:101166. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101166. eCollection 2024 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39189016 Free PMC article.
-
Inorganic and hybrid nanomaterials for NIR-II fluorescence imaging-guided therapy of Glioblastoma and perspectives.Theranostics. 2025 Apr 21;15(12):5616-5665. doi: 10.7150/thno.112204. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40365286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional Upconversion Nanoparticles Transforming Photoacoustic Imaging: A Review.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Jul 10;15(14):1074. doi: 10.3390/nano15141074. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40711193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Functionalized Nanoparticles for Osteoporosis Treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 20;20:7869-7891. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S519945. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40557247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Water-insensitive NIR-I-to-NIR-I down-shifting nanoparticles enable stable biomarker detection at low power thresholds in opaque aqueous environments.Light Sci Appl. 2025 Jul 3;14(1):235. doi: 10.1038/s41377-025-01882-2. Light Sci Appl. 2025. PMID: 40610419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Y., Zang P., Yang D., Zhang R., Gai S., Yang P., Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 1140. - PubMed
-
- Lei P., An R., Zhang P., Yao S., Song S., Dong L., Xu X., Du K., Feng J., Zhang H., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702018.
-
- Du P., An R., Liang Y., Lei P., Zhang H., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 471, 214745.
-
- Zheng B., Fan J., Chen B., Qin X., Wang J., Wang F., Deng R., Liu X., Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
