Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of daratumumab in the treatment of multiple myeloma
- PMID: 37946760
- PMCID: PMC10631397
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i29.7091
Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of daratumumab in the treatment of multiple myeloma
Abstract
Background: The treatment of multiple myeloma has significantly progressed over the past half-century. The purpose of this study was to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis in order to explore the efficacy and safety of daratumumab in treating multiple myeloma.
Aim: To explore the efficacy and safety of daratumumab in treating multiple myeloma.
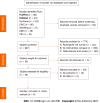
Methods: A systematic literature search was performed using Chinese and English databases, including the China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang, China Biology Medicine, VIP, the Cochrane Library, Embase, and PubMed. The search encompassed studies in treating multiple myeloma with daratumumab, spanning from the inception of the database to June 2023. Revman 5.1 software was used for analysis.
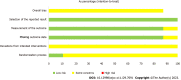
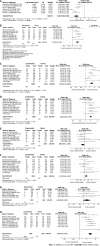
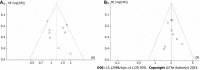
Results: Our analysis included eight English articles and one Chinese article of high quality. The meta-analysis results indicated that compared to other therapies, daratumumab could improve the overall response rate (ORR) [odds ratio (OR) = 2.67, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 2.01, 3.53, Z = 6.85, P < 0.00001], complete remission (CR) (OR = 2.87, 95%CI = 2.16, 3.83, Z = 7.23, P < 0.00001) and progression-free survival (PFS) time (hazard ratio = 0.48, 95%CI = 0.38,0.60, Z = 6.54, P < 0.00001) in patients with multiple myeloma. These differences were statistically significant. Additionally, these results suggested that daratumumab increases the risk of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia with minimal effect on the incidences of anemia and upper respiratory tract infections.
Conclusion: Daratumumab can improve ORR, CR rate, and PFS in patients with multiple myeloma. It also increases the risk of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia, necessitating careful monitoring during its clinical application.
Keywords: Daratumumab; Efficacy; Meta-analysis; Multiple myeloma; Safety.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All author reports have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bahlis NJ, Dimopoulos MA, White DJ, Benboubker L, Cook G, Leiba M, Ho PJ, Kim K, Takezako N, Moreau P, Kaufman JL, Krevvata M, Chiu C, Qin X, Okonkwo L, Trivedi S, Ukropec J, Qi M, San-Miguel J. Daratumumab plus lenalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: extended follow-up of POLLUX, a randomized, open-label, phase 3 study. Leukemia. 2020;34:1875–1884. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulos M, Quach H, Mateos MV, Landgren O, Leleu X, Siegel D, Weisel K, Yang H, Klippel Z, Zahlten-Kumeli A, Usmani SZ. Carfilzomib, dexamethasone, and daratumumab vs carfilzomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (CANDOR): results from a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2020;396:186–197. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

