Hemoglobin A1c as a Predictor of Surgical Site Infection in Patients With Orthopaedic Trauma
- PMID: 37947426
- PMCID: PMC10635592
- DOI: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-23-00204
Hemoglobin A1c as a Predictor of Surgical Site Infection in Patients With Orthopaedic Trauma
Abstract
Introduction: Previous research involving diabetes mellitus (DM), glycemic control, and complications in orthopaedic patients has primarily focused on elective procedures. The purpose of this study was to evaluate hemoglobin A1c (A1c) as a predictor of postoperative surgical site infection (SSI) in patients with orthopaedic trauma.
Methods: Patients aged 18 years or older treated surgically for an acute fracture by a fellowship-trained orthopaedic trauma surgeon at a single academic tertiary referral center with a laboratory value for A1c available within 3 months of their surgery were identified retrospectively. Postoperative SSI was defined according to 'Fracture related infection: A consensus on definition from an international expert group,' by Metsemakers et al.
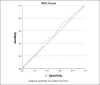
Results: A total of 925 patients met criteria for analysis. A receiver operating characteristic curve was calculated using A1c as a predictor for signs suggestive and confirmatory of SSI and demonstrated an area under the curve of 0.535 and 0.539, respectively. No significant difference was found in the rate of signs suggestive or confirmatory of SSI in patients with normal A1c levels (<6.5) compared with patients with A1c levels consistent with a diagnosis of DM (>6.5), P-value = 0.199 and P-value = 0.297, respectively. No significant difference was found in the rate of signs suggestive or confirmatory of SSI in patients with completely uncontrolled DM (A1c > 10) compared with patients with A1c levels <10, P-value 0.528 and P-value = 0.552, respectively.
Conclusion: Existing literature has demonstrated an association with postoperative infection in orthopaedic patients who have elevated A1c values. In this cohort of patients with orthopaedic trauma, hemoglobin A1c was not a valuable tool to predict postoperative SSI. Given these findings, routine A1c monitoring is not a reliable predictor of SSI criteria in patients with orthopaedic trauma based on the current consensus definition of SSI in fracture surgery.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National diabetes statistical report, 2020, Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html, Accessed November 13, 2020.
-
- Cancienne JM, Werner BC, Browne JA: Is there a threshold value of hemoglobin A1c that predicts risk of infection following primary total hip arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty 2017;32:S236-S240. - PubMed
-
- Chrastil J, Anderson MB, Stevens V, Anand R, Peters CL, Pelt CE: Is hemoglobin A1c or perioperative hyperglycemia predictive of periprosthetic joint infection or death following primary total joint arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty 2015;30:1197-1202. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

