Stress-induced β cell early senescence confers protection against type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 37949065
- PMCID: PMC10842515
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.10.014
Stress-induced β cell early senescence confers protection against type 1 diabetes
Abstract
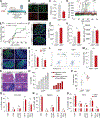
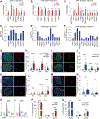
During the progression of type 1 diabetes (T1D), β cells are exposed to significant stress and, therefore, require adaptive responses to survive. The adaptive mechanisms that can preserve β cell function and survival in the face of autoimmunity remain unclear. Here, we show that the deletion of the unfolded protein response (UPR) genes Atf6α or Ire1α in β cells of non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice prior to insulitis generates a p21-driven early senescence phenotype and alters the β cell secretome that significantly enhances the leukemia inhibitory factor-mediated recruitment of M2 macrophages to islets. Consequently, M2 macrophages promote anti-inflammatory responses and immune surveillance that cause the resolution of islet inflammation, the removal of terminally senesced β cells, the reduction of β cell apoptosis, and protection against T1D. We further demonstrate that the p21-mediated early senescence signature is conserved in the residual β cells of T1D patients. Our findings reveal a previously unrecognized link between β cell UPR and senescence that, if leveraged, may represent a novel preventive strategy for T1D.
Keywords: ER stress; M2 macrophage; NOD mice; UPR; immune surveillance; secretome; senescence; type 1 diabetes; β cells.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Protocol for quantifying SA-β-gal activity as a measure of senescence in islets of a mouse model of type 1 diabetes.STAR Protoc. 2024 Mar 15;5(1):102923. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2024.102923. Epub 2024 Feb 29. STAR Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38427571 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

