Unraveling the optoelectronic properties of CoSbx intrinsic selective solar absorber towards high-temperature surfaces
- PMID: 37949914
- PMCID: PMC10638324
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42839-6
Unraveling the optoelectronic properties of CoSbx intrinsic selective solar absorber towards high-temperature surfaces
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Unraveling the optoelectronic properties of CoSbx intrinsic selective solar absorber towards high-temperature surfaces.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 26;15(1):3548. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47332-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38670951 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
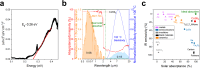
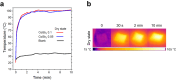
The combination of the ability to absorb most of the solar radiation and simultaneously suppress infrared re-radiation allows selective solar absorbers (SSAs) to maximize solar energy to heat conversion, which is critical to several advanced applications. The intrinsic spectral selective materials are rare in nature and only a few demonstrated complete solar absorption. Typically, intrinsic materials exhibit high performances when integrated into complex multilayered solar absorber systems due to their limited spectral selectivity and solar absorption. In this study, we propose CoSbx (2 < x < 3) as a new exceptionally efficient SSA. Here we demonstrate that the low bandgap nature of CoSbx endows broadband solar absorption (0.96) over the solar spectral range and simultaneous low emissivity (0.18) in the mid-infrared region, resulting in a remarkable intrinsic spectral solar selectivity of 5.3. Under 1 sun illumination, the heat concentrates on the surface of the CoSbx thin film, and an impressive temperature of 101.7 °C is reached, demonstrating the highest value among reported intrinsic SSAs. Furthermore, the CoSbx was tested for solar water evaporation achieving an evaporation rate of 1.4 kg m-2 h-1. This study could expand the use of narrow bandgap semiconductors as efficient intrinsic SSAs with high surface temperatures in solar applications.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Fan X, et al. A MXene-based hierarchical design enabling highly efficient and stable solar-water desalination with good salt resistance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020;30:1–11. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202007110. - DOI
-
- Zhou L, et al. Self-assembled spectrum selective plasmonic absorbers with tunable bandwidth for solar energy conversion. Nano Energy. 2017;32:195–200. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.12.031. - DOI
-
- Ni G, et al. Steam generation under one sun enabled by a floating structure with thermal concentration. Nat. Energy. 2016;1:1–7. doi: 10.1038/nenergy.2016.126. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

