Impact of low serum iron on treatment outcome of PD-1 inhibitors in advanced gastric cancer
- PMID: 37950201
- PMCID: PMC10638799
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-023-11620-9
Impact of low serum iron on treatment outcome of PD-1 inhibitors in advanced gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to investigate the influence of serum iron levels in advanced gastric cancer (GC) patients treated with programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) inhibitors.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 149 GC patients who were treated with PD-1 inhibitors at our center. Clinicopathological characteristics, laboratory data, and clinical outcomes were analyzed.
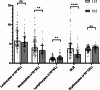
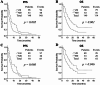
Results: Multivariate analysis showed that Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS), histological subtype, and baseline serum iron levels were independent prognostic factors for overall survival (OS), while ECOG PS, multiple metastatic sites, and baseline serum iron levels were independent prognostic factors for progression-free survival (PFS). Patients with baseline low serum iron levels (LSI) had a significantly shorter median OS and PFS compared to patients with normal serum iron levels (NSI) (Median OS: 7 vs. 14 months, p = 0.001; median PFS: 3 vs. 5 months, p = 0.005). Patients with baseline LSI had a disease control rate (DCR) of 58.3% at 2 months after PD-1 inhibitor initiation (M2), compared to 81.1% in patients with NSI (p = 0.005). Patients with baseline LSI had a DCR of 43.8% at 4 months, compared to 64.2% in patients with NSI (p = 0.017).
Conclusions: LSI was associated with worse OS, PFS, and DCR in GC patients treated with PD-1 inhibitors and might be a quick and efficient biomarker to predict the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors.
Keywords: Biomarker; Gastric cancer; Immune checkpoint inhibitor; Serum iron.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Saint A, Viotti J, Borchiellini D, Hoch B, Raimondi V, Hebert C, Largillier R, Evesque L, Follana P, Ferrero JM, et al. Iron Deficiency during first-line chemotherapy in metastatic cancers: a prospective epidemiological study. Supportive care in cancer: Official Journal of the Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer. 2020;28(4):1639–47. doi: 10.1007/s00520-019-04938-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

