Perception, attitude, and practice toward research among medical students in Hadhramout University, Yemen
- PMID: 37950269
- PMCID: PMC10638770
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-023-04287-0
Perception, attitude, and practice toward research among medical students in Hadhramout University, Yemen
Abstract
Background: Research is an important element in the improvement of the quality of health services provided to the public. It is documented that globally; medical students apply research in their school life. In Hadhramaut University, medical students work on research in groups, and it is an important part of the curriculum. There is a formal assessment of the student's research, but there is still a gap regarding individual viewpoints and challenges faced. This study aimed to assess perception, attitude, and practice toward research among medical students at Hadhramout University.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional descriptive study which was conducted among medical students. This study was undertaken in Hadhramout University in Al-Mukalla district, Yemen, during the academic year 2016-2017. A self-administered pilot-tested questionnaire was used for data collection to assess perception, attitude, and practice toward the research during the educational year 2016-2017.
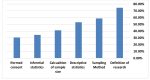
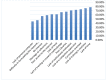
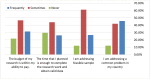
Results: A total of 265 completed responses were received. The majority had a low Knowledge score (72%). However, the majority had a positive attitude toward research (90.9%). Eighty-three students reported participation in research work. However, (44.4%) expressed research interest. Many barriers were highlighted by students including a lack of time (78.4%) and a lack of training in statistics (75.9%).
Conclusion: The study identified several barriers for undergraduate medical students to undertake research. It is important that these barriers should be addressed in curriculum development, so that students can retain their motivation to engage effectively in research.
Keywords: Medical students; Undergraduate research; Yemen.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- GetuDegu and TegbarYigzaw . Research Methodology. Ethiopia: University of Gondar; 2006.
-
- Amin TT, Kaliyadan F, Al Gattan EA, AlMjed MH. Al khanjaf h S and Mirza M. Knowledge, attitudes and barriers related to participation of medical students in research in three arab universities. Educ Med J. 2012;4(1). 10.5959/eimj.v4i1.7. (Accessed 20/2/2017).
-
- Madhur G, Arti. A.Awareness of research among dental students in India. Journal of evaluation of medical & dental science. 2014; 3:25. Doi: 10.14260/jemds/2014/2840. (Accessed 17/2/2017).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous