Dark Blood Contrast-Enhanced Brain MRI Using Echo-uT1RESS
- PMID: 37950398
- PMCID: PMC11087375
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.29124
Dark Blood Contrast-Enhanced Brain MRI Using Echo-uT1RESS
Abstract
Background: The widely used magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo (MPRAGE) sequence makes enhancing lesions and blood vessels appear bright after gadolinium administration. However, dark blood imaging using T1-weighted Sampling Perfection with Application optimized Contrast using different flip angle Evolution (T1 SPACE) can be advantageous since it improves the conspicuity of small metastases and leptomeningeal disease. As a potential alternative to T1 SPACE, we evaluated a new dark blood sequence called echo-uT1RESS (unbalanced T1 Relaxation-Enhanced Steady-State).
Purpose: We compared the performance of echo-uT1RESS with Dixon fid-uT1RESS, MPRAGE, and T1 SPACE.
Study type: Retrospective, IRB approved.
Subjects/phantom: Phantom to assess flow properties of echo-uT1RESS. Twenty-one patients (14 female, age range 35-82 years) with primary and secondary brain tumors.
Field strength/sequences: 3 Tesla/MPRAGE, T1 SPACE, Dixon fid-uT1RESS, echo-uT1RESS.
Assessment: Flow phantom signal vs. velocity as a function of flip angle and sequence. Qualitative image assessment on 4-point scale. Quantitative evaluation of tumor-to-brain contrast, apparent contrast-to-noise ratio (aCNR), and vessel-to-brain aCNR.
Statistical tests: Friedman and Mann-Whitney U tests. A P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
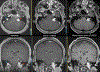
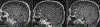
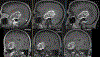
Results: In the phantom, echo-uT1RESS showed greater flow-dependent signal loss than fid-uT1RESS. In patients, blood vessels appeared bright with MPRAGE, gray with fid-uT1RESS, and dark with T1 SPACE and echo-uT1RESS. For MPRAGE, Dixon fid-uT1RESS, echo-uT1RESS, and T1 SPACE, respective tumor-to-brain contrast values were 0.6 ± 0.3, 1.3 ± 0.5, 1.0 ± 0.4, and 0.6 ± 0.4, while normalized aCNR values were 68.9 ± 50.9, 128.4 ± 59.2, 74.2 ± 42.1, and 99.4 ± 73.9.
Data conclusion: Volumetric dark blood contrast-enhanced brain MRI is feasible using echo-uT1RESS. The dark blood effect was improved vs. fid-uT1RESS, while both uT1RESS versions provided better tumor-to-brain contrast than MPRAGE. Whereas T1 SPACE provided better tumor aSNR, echo-uT1RESS provided better Weber contrast, lesion sharpness and a more consistent dark blood effect.
Evidence level: 3 TECHNICAL EFFICACY: Stage 1.
Keywords: brain tumor; contrast enhancement; dark blood MRI; fast imaging with steady‐state free precession; unbalanced T1 relaxation‐enhanced steady‐state.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures
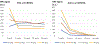



Comment in
-
Editorial for "Dark Blood Contrast-Enhanced Brain MRI Using Echo-uT1RESS".J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Aug;60(2):798-799. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29125. Epub 2023 Nov 11. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37950605 No abstract available.
References
-
- Langen KJ, Galldiks N, Hattingen E, Shah NJ. Advances in neuro-oncology imaging. Nat Rev Neurol 2017;13(5):279–289. - PubMed
-
- Mugler JP 3rd, Brookeman JR. Three-dimensional magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo imaging (3D MP RAGE). Magn Reson Med 1990;15(1):152–157. - PubMed
-
- Kato Y, Higano S, Tamura H, et al. Usefulness of contrast-enhanced T1-weighted sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts by using different flip angle evolutions in detection of small brain metastasis at 3T MR imaging: comparison with magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition of gradient echo imaging. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology 2009;30(5):923–929. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

