Treatment of myopic choroidal neovascularization: a network meta-analysis and review
- PMID: 37950753
- PMCID: PMC11106160
- DOI: 10.1007/s00417-023-06271-2
Treatment of myopic choroidal neovascularization: a network meta-analysis and review
Abstract
Purpose: This is, to our knowledge, the first network meta-analysis aiming to compare all treatment modalities for myopic choroidal neovascularization (CNV).
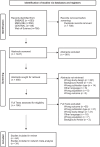
Methods: After the electronic databases were searched, two independent reviewers screened titles, abstracts, full-texts, and extracted information. Primary endpoints were change in visual outcome and central retinal thickness. We used a network meta-analysis to compare treatment outcomes in the early (≤ 6 months) and late (> 6 months) phase.
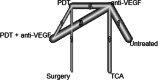
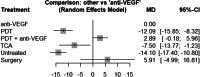
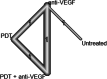
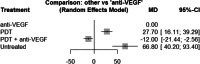
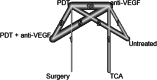
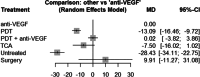
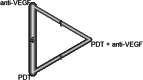
Results: We included 34 studies (2,098 eyes) in our network meta-analysis. In the early phase, the use of anti-VEGF led to a gain of 14.1 letters (95% CI, 10.8-17.4) compared to untreated patients (p < 0.0001), 12.1 letters (95% CI, 8.3-15.8) to photodynamic therapy (PDT) (p < 0.0001), 7.5 (95% CI, 1.2-13.8) letters to intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide (TCA) (p = 0.019), and - 2.9 letters (95% CI, - 6.0-0.2) to the combination of anti-VEGF and PDT (p = 0.065). In the later phase, these results were largely maintained. There were no significant differences in visual outcomes between patients treated with 1 + PRN and 3 + PRN. However, the 1 + PRN group received 1.8 (SD 1.3), while the 3 + PRN group received 3.2 (SD 0.9) injections within 12 months (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: This network meta-analysis confirms that anti-VEGF is the most effective treatment for myopic CNV using the 1 + PRN treatment strategy.
Keywords: Aflibercept; Anti-VEGF; Bevacizumab; Choroidal neovascularization; Conbercept; Myopia; Myopic CNV; Photodynamic therapy; Ranibizumab.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Blinder KJ, Blumenkranz MS, Bressler NM, Bressler SB, Donati G, Lewis H, Lim JI, Menchini U, Miller JW, Mones JM, Potter MJ, Pournaras C, Reaves A, Rosenfeld P, Schachat AP, Schmidt-Erfurth U, Sickenberg M, Singerman LJ, Slakter JS, Strong HA, Virgili G, Williams GA. Verteporfin therapy of subfoveal choroidal neovascularization in pathologic myopia: 2-year results of a randomized clinical trial - VIP report no. 3. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:667–673. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(02)01998-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Miller JW, Vavvas D, Kim IK. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monotherapy versus combination treatment with photodynamic therapy for subfoveal choroidal neovascularization secondary to causes other than age-related macular degeneration. Retin-J Retin Vitr Dis. 2011;31:2078–2083. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3182109074. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

