RNF14-dependent atypical ubiquitylation promotes translation-coupled resolution of RNA-protein crosslinks
- PMID: 37951216
- PMCID: PMC10783637
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.10.012
RNF14-dependent atypical ubiquitylation promotes translation-coupled resolution of RNA-protein crosslinks
Abstract
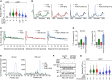
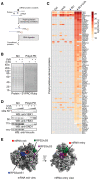
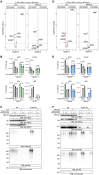
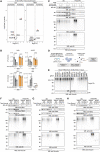
Reactive aldehydes are abundant endogenous metabolites that challenge homeostasis by crosslinking cellular macromolecules. Aldehyde-induced DNA damage requires repair to prevent cancer and premature aging, but it is unknown whether cells also possess mechanisms that resolve aldehyde-induced RNA lesions. Here, we establish photoactivatable ribonucleoside-enhanced crosslinking (PAR-CL) as a model system to study RNA crosslinking damage in the absence of confounding DNA damage in human cells. We find that such RNA damage causes translation stress by stalling elongating ribosomes, which leads to collisions with trailing ribosomes and activation of multiple stress response pathways. Moreover, we discovered a translation-coupled quality control mechanism that resolves covalent RNA-protein crosslinks. Collisions between translating ribosomes and crosslinked mRNA-binding proteins trigger their modification with atypical K6- and K48-linked ubiquitin chains. Ubiquitylation requires the E3 ligase RNF14 and leads to proteasomal degradation of the protein adduct. Our findings identify RNA lesion-induced translational stress as a central component of crosslinking damage.
Keywords: GCN1; K6-linked ubiquitin chains; RNA damage; RNA-protein crosslinks; RNF14; RNF25; atypical ubiquitylation; formaldehyde; ribosome; translation.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.G. is a member of the scientific advisory board at the journal Molecular Cell.
Figures




Comment in
-
Atypical K6-ubiquitin chains mobilize p97/VCP and the proteasome to resolve formaldehyde-induced RNA-protein crosslinks.Mol Cell. 2023 Dec 7;83(23):4197-4199. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.11.009. Mol Cell. 2023. PMID: 38065058
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

