Skeletal muscle TFEB signaling promotes central nervous system function and reduces neuroinflammation during aging and neurodegenerative disease
- PMID: 37952157
- PMCID: PMC10841857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113436
Skeletal muscle TFEB signaling promotes central nervous system function and reduces neuroinflammation during aging and neurodegenerative disease
Abstract
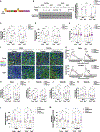
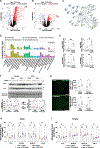
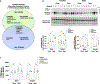
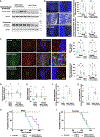
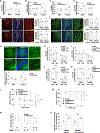
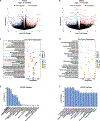
Skeletal muscle has recently arisen as a regulator of central nervous system (CNS) function and aging, secreting bioactive molecules known as myokines with metabolism-modifying functions in targeted tissues, including the CNS. Here, we report the generation of a transgenic mouse with enhanced skeletal muscle lysosomal and mitochondrial function via targeted overexpression of transcription factor E-B (TFEB). We discovered that the resulting geroprotective effects in skeletal muscle reduce neuroinflammation and the accumulation of tau-associated pathological hallmarks in a mouse model of tauopathy. Muscle-specific TFEB overexpression significantly ameliorates proteotoxicity, reduces neuroinflammation, and promotes transcriptional remodeling of the aged CNS, preserving cognition and memory in aged mice. Our results implicate the maintenance of skeletal muscle function throughout aging in direct regulation of CNS health and disease and suggest that skeletal muscle originating factors may act as therapeutic targets against age-associated neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; TFEB; aging; brain; exercise; muscle; neurodegeneration; tau.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Rai M, Coleman Z, Curley M, Nityanandam A, Platt A, Robles-Murguia M, Jiao J, Finkelstein D, Wang YD, Xu B, et al. (2021). Proteasome stress in skeletal muscle mounts a long-range protective response that delays retinal and brain aging. Cell Metab. 33, 1137–1154.e9. 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.03.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

