Exploiting public databases of genomic variation to quantify evolutionary constraint on the branch point sequence in 30 plant and animal species
- PMID: 37953306
- PMCID: PMC10711541
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad970
Exploiting public databases of genomic variation to quantify evolutionary constraint on the branch point sequence in 30 plant and animal species
Abstract
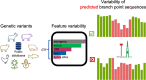
The branch point sequence is a degenerate intronic heptamer required for the assembly of the spliceosome during pre-mRNA splicing. Disruption of this motif may promote alternative splicing and eventually cause phenotype variation. Despite its functional relevance, the branch point sequence is not included in most genome annotations. Here, we predict branch point sequences in 30 plant and animal species and attempt to quantify their evolutionary constraints using public variant databases. We find an implausible variant distribution in the databases from 16 of 30 examined species. Comparative analysis of variants from whole-genome sequencing shows that variants submitted from exome sequencing or false positive variants are widespread in public databases and cause these irregularities. We then investigate evolutionary constraint with largely unbiased public variant databases in 14 species and find that the fourth and sixth position of the branch point sequence are more constrained than coding nucleotides. Our findings show that public variant databases should be scrutinized for possible biases before they qualify to analyze evolutionary constraint.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The intronic branch point sequence is under strong evolutionary constraint in the bovine and human genome.Commun Biol. 2021 Oct 21;4(1):1206. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02725-7. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34675361 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic Abnormal Splicing Due to Intronic Deletions that Induce Biophysical Space Constraint for Spliceosome Assembly.Am J Hum Genet. 2019 Sep 5;105(3):573-587. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.07.013. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Am J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31447096 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary convergence on highly-conserved 3' intron structures in intron-poor eukaryotes and insights into the ancestral eukaryotic genome.PLoS Genet. 2008 Aug 8;4(8):e1000148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000148. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18688272 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of minor spliceosome in intron recognition and the convergence with the better understood major spliceosome.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Jan;14(1):e1761. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1761. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 36056453 Review.
-
Splicing of precursors to mRNA in higher plants: mechanism, regulation and sub-nuclear organisation of the spliceosomal machinery.Plant Mol Biol. 1996 Oct;32(1-2):1-41. doi: 10.1007/BF00039375. Plant Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8980472 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-DNA differences in variant calls from cattle tissues result in erroneous eQTLs.BMC Genomics. 2024 Aug 1;25(1):750. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10645-z. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39090567 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

