Evaluation of the hydroalcoholic extract of Clarisia racemosa as an antiparasitic agent: an in vitro approach
- PMID: 37953832
- PMCID: PMC10635994
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03799-2
Evaluation of the hydroalcoholic extract of Clarisia racemosa as an antiparasitic agent: an in vitro approach
Abstract
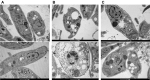
Clarisia racemosa Ruiz & Pav is a neotropical species found in humid forests from southern Mexico to southern Brazil. There are few studies related to the ethnopharmacological use of C. racemosa. Our objective was to evaluate the hydroalcoholic extract of C. racemosa as a potential antiparasitic agent. For this, we performed in vitro assays against strains of Leishmania amazonensis, Trypanosoma cruzi, Plasmodium falciparum, and Schistosoma mansoni. At the same time, immunomodulatory activity tests were carried out. The results demonstrated that the extract was able to stimulate and activate immune cells. In preliminary antiparasitic tests, structural modifications were observed in the promastigote form of L. amazonensis and in adult worms of S. mansoni. The extract was able to inhibit the growth of trypomastigote form of T. cruzi and finally showed low antiparasitic activity against strains of P. falciparum. It is pioneering work and these results demonstrate that C. racemosa extract is a promising alternative and contributes to the arsenal of possible forms of treatment to combat parasites.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13205-023-03799-2.
Keywords: Amazon forest; Antiparasitic agent; Clarisia racemosa; Natural products.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could appear to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures




References
-
- Abd-Allah M, Abdelwahab M, Aly NS, Amer OS, Sarhan M. In vitro schistosomicidal activity of five common species of red sea cone snail muscle extracts. Al-Azhar Bull Sci. 2022;33(2C):111–119. doi: 10.21608/ABSB.2022.140291.1187. - DOI
-
- Albuquerque Nerys LL, Jacob ITT, Silva AR, Oliveira AM, Rocha WRV, Pereira DTM, Lima MDCA. Photoprotective, biological activities and chemical composition of the non-toxic hydroalcoholic extract of Clarisia racemosa with cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications. Ind Crops Prod. 2022;180:114762. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114762. - DOI
-
- Araújo DMF, Cruz Filho IJ, Santos T, Pereira DTM, Marques DSC, de Lima ADCA, Nogueira F. Biological activities and physicochemical characterization of alkaline lignins obtained from branches and leaves of Buchenavia viridiflora with potential pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;219:224–245. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.225. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barusrux S, Phiboonchaiyanan PP, Khamphio M, Weerapreeyakul N, Siriamornpun S. Effects of jujube fruit extract on peripheral blood mononuclear cell proliferation, cytokine productions and intracellular hydrogen peroxide level. Walailak J Sci Technol (WJST) 2018;15(8):561–568. doi: 10.48048/wjst.2018.4595. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

