Nectar robbing by bees affects the reproductive fitness of the distylous plant Tirpitzia sinensis (Linaceae)
- PMID: 37953984
- PMCID: PMC10638493
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.10714
Nectar robbing by bees affects the reproductive fitness of the distylous plant Tirpitzia sinensis (Linaceae)
Abstract
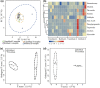
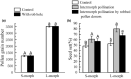
Nectar robbing can affect plant reproductive success directly by influencing female and male fitness, and indirectly by affecting pollinator behavior. Flowers have morphological and chemical features that may protect them from nectar robbers. Previous studies on nectar robbing have focused mainly on homotypic plants. It remains unclear how nectar robbing affects the reproductive success of distylous plants, and whether defense strategies of two morphs are different. Nectar-robbing rates on the long- and short-styled morph (L-morph, S-morph) of the distylous Tirpitzia sinensis were investigated. We compared floral traits, the temporal pattern of change in nectar volume and sugar concentration, nectar secondary metabolites, and sugar composition between robbed and unrobbed flowers of two morphs. We tested direct effects of nectar robbing on female and male components of plant fitness and indirect effects of nectar robbing via pollinators. Nectar-robbing rates did not differ between the two morphs. Flowers with smaller sepals and petals were more easily robbed. The floral tube diameter and thickness were greater in L-morphs than in S-morphs, and the nectar rob holes were significantly smaller in L-morphs than in S-morphs. Nectar robbing significantly decreased nectar replenishment rate but did not affect nectar sugar concentration or sugar composition. After robbery, the quantities and diversity of secondary compounds in the nectar of S-morphs increased significantly and total relative contents of secondary compounds in L-morphs showed no obvious changes. Nectar robbing could decrease female fitness by decreasing pollen germination rate and thus decreasing seed set. Nectar robbing had no significant effects on male fitness. Robbed flowers were less likely to be visited by hawkmoth pollinators, especially in S-morphs. These results suggest that nectar robbing could directly and indirectly decrease the female fitness of T. sinensis, and different morphs have evolved different defense mechanisms in response to nectar-robbing pressure.
Keywords: defense strategies; distyly; nectar robbing; plant fitness; reproductive success.
© 2023 The Authors. Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Agrawal, A. A. , Hastings, A. P. , Johnson, M. T. J. , Maron, J. L. , & Salminen, J. P. (2012). Insect herbivores drive real‐time ecological and evolutionary change in plant populations. Science, 338, 113–116. - PubMed
-
- Barlow, S. E. , Wright, G. A. , Ma, C. , Barberis, M. , Farrell, I. W. , Marr, E. C. , Brankin, A. , Pavlik, B. M. , & Stevenson, P. C. (2017). Distasteful nectar deters floral robbery. Current Biology, 27, 2552–2558. - PubMed
-
- Barrett, S. C. H. , & Shore, J. S. (2008). New insights on heterostyly: Comparative biology, ecology and genetics. In Franklin‐Tong V. E. (Ed.), Self‐incompatibility in flowering plants (pp. 3–261). Springer.
-
- Becerra, J. X. , Venable, D. L. , Evans, P. H. , & Bowers, W. S. (2001). Interactions between chemical and mechanical defenses in the plant genus Bursera and their implications for herbivores. American Zoologist, 41, 865–876.
-
- Bronstein, J. L. , Barker, J. L. , Lichtenberg, E. M. , Richardson, L. L. , & Irwin, R. E. (2017). The behavioral ecology of nectar robbing: Why be tactic constant? Current Opinion in Insect Science, 21, 14–18. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

