CT-based dosiomics and radiomics model predicts radiation-induced lymphopenia in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients
- PMID: 37954080
- PMCID: PMC10634512
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1168995
CT-based dosiomics and radiomics model predicts radiation-induced lymphopenia in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to develop and validate a model predictive for the incidence of grade 4 radiation-induced lymphopenia (G4RIL), based on dosiomics features and radiomics features from the planning CT of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) treated by radiation therapy.
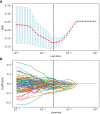
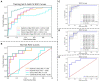
Methods: The dataset of 125 NPC patients treated with radiotherapy from August 2018 to March 2019 was randomly divided into two sets-an 85-sample training set and a 40-sample test set. Dosiomics features and radiomics features of the CT image within the skull bone and cervical vertebrae were extracted. A feature selection process of multiple steps was employed to identify the features that most accurately forecast the data and eliminate superfluous or insignificant ones. A support vector machine learning classifier with correction for imbalanced data was trained on the patient dataset for prediction of RIL (positive classifier for G4RIL, negative otherwise). The model's predictive capability was gauged by gauging its sensitivity (the likelihood of a positive test being administered to patients with G4RIL) and specificity in the test set. The area beneath the ROC curve (AUC) was utilized to explore the association of characteristics with the occurrence of G4RIL.
Results: Three clinical features, three dosiomics features, and three radiomics features exhibited significant correlations with G4RIL. Those features were then used for model construction. The combination model, based on nine robust features, yielded the most impressive results with an ACC value of 0.88 in the test set, while the dosiomics model, with three dosiomics features, had an ACC value of 0.82, the radiomics model, with three radiomics features, had an ACC value of 0.82, and the clinical model, with its initial features, had an ACC value of 0.6 for prediction performance.
Conclusion: The findings show that radiomics and dosiomics features are correlated with the G4RIL of NPC patients. The model incorporating radiomics features and dosiomics features from planning CT can predict the incidence of G4RIL in NPC patients.
Keywords: dosiomics; machine learning; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; radiation-induced lymphopenia; radiomics.
Copyright © 2023 Huang, Yang, Pang, Zeng, Yang, Zhou, Wu, Shen, Zhang, Lou, Jin, Abdilim, Jin, Zhang and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Deep learning dosiomics in grade 4 radiation-induced lymphopenia prediction in radiotherapy for esophageal cancer: a multi-center study.Radiother Oncol. 2025 Aug;209:110995. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2025.110995. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Radiother Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40550423
-
Dosiomics and radiomics improve the prediction of post-radiotherapy neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Med Phys. 2024 Jan;51(1):650-661. doi: 10.1002/mp.16829. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 37963229
-
Multi-omics to predict acute radiation esophagitis in patients with lung cancer treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Mar 19;28(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01041-6. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 36935504 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Radiomics- and Dosiomics-based Predicting Models for Rectal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 9;12:913683. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.913683. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36016617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiomics-based hybrid model for predicting radiation pneumonitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Phys Med. 2024 Jul;123:103414. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2024.103414. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Phys Med. 2024. PMID: 38906047
Cited by
-
Delta radiomics: an updated systematic review.Radiol Med. 2024 Aug;129(8):1197-1214. doi: 10.1007/s11547-024-01853-4. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Radiol Med. 2024. PMID: 39017760 Free PMC article.
-
Do We Need to Add the Type of Treatment Planning System, Dose Calculation Grid Size, and CT Density Curve to Predictive Models?Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 20;15(6):786. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060786. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150128 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

