Therapeutic Advantage of Targeting PRMT5 in Combination with Chemotherapies or EGFR/HER2 Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers
- PMID: 37954171
- PMCID: PMC10637385
- DOI: 10.2147/BCTT.S430513
Therapeutic Advantage of Targeting PRMT5 in Combination with Chemotherapies or EGFR/HER2 Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers
Abstract
Purpose: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive breast cancer subgroup characterized by a high risk of resistance to chemotherapies and high relapse potential. TNBC shows inter-and intra-tumoral heterogeneity; more than half expresses high EGFR levels and about 30% are classified as HER2-low breast cancers. High PRMT5 mRNA levels are associated with poor prognosis in TNBC and inhibiting PRMT5 impairs the viability of subsets of TNBC cell lines and delays tumor growth in TNBC mice models. TNBC patients may therefore benefit from a treatment targeting PRMT5. The aim of this study was to assess the therapeutic benefit of combining a PRMT5 inhibitor with different chemotherapies used in the clinics to treat TNBC patients, or with FDA-approved inhibitors targeting the HER family members.
Methods: The drug combinations were performed using proliferation and colony formation assays on TNBC cell lines that were sensitive or resistant to EPZ015938, a PRMT5 inhibitor that has been evaluated in clinical trials. The chemotherapies analyzed were cisplatin, doxorubicin, camptothecin, and paclitaxel. The targeted therapies tested were erlotinib (EGFR inhibitor), neratinib (EGFR/HER2/HER4 inhibitor) and tucatinib (HER2 inhibitor).
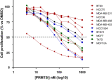
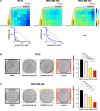
Results: We found that PRMT5 inhibition synergized mostly with cisplatin, and to a lesser extent with doxorubicin or camptothecin, but not with paclitaxel, to impair TNBC cell proliferation. PRMT5 inhibition also synergized with erlotinib and neratinib in TNBC cell lines, especially in those overexpressing EGFR. Additionally, a synergistic interaction was observed with neratinib and tucatinib in a HER2-low TNBC cell line as well as in a HER2-positive breast cancer cell line. We noticed that synergy can be obtained in TNBC cell lines that were resistant to PRMT5 inhibition alone.
Conclusion: Altogether, our data highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting PRMT5 using combinatorial strategies for the treatment of subsets of TNBC patients.
Keywords: TNBC; cisplatin; drug combination; erlotinib; neratinib.
© 2023 Dakroub et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protein arginine methyltransferase 5: A novel therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancers.Cancer Med. 2019 May;8(5):2414-2428. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2114. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 30957988 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K and MAPK Pathways as Targets for Combination with the Pan-HER Irreversible Inhibitor Neratinib in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer and TNBC by Kinome RNAi Screening.Biomedicines. 2021 Jun 28;9(7):740. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070740. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34203351 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting EGFR of triple-negative breast cancer enhances the therapeutic efficacy of paclitaxel- and cetuximab-conjugated nanodiamond nanocomposite.Acta Biomater. 2019 Mar 1;86:395-405. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.01.025. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30660004
-
A perspective on anti-EGFR therapies targeting triple-negative breast cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2016 Aug 1;6(8):1609-23. eCollection 2016. Am J Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27648353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Current Treatment Strategies, Unmet Needs, and Potential Targets for Future Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 24;12(9):2392. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092392. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32846967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PRMT5 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in MYC-Amplified Medulloblastoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 15;15(24):5855. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245855. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody-drug conjugates in breast cancer treatment: resistance mechanisms and the role of therapeutic sequencing.Cancer Drug Resist. 2025 Mar 6;8:11. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.180. eCollection 2025. Cancer Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40201309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic targeting of protein arginine methyltransferases reduces breast cancer progression by disrupting angiogenic pathways.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Jul 31;43:102172. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102172. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40791817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

