Meta-analysis of the efficacy of budesonide and ambroxol hydrochloride inhalation in children with pneumonia and their effects on inflammatory response
- PMID: 37954384
- PMCID: PMC10637922
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21105
Meta-analysis of the efficacy of budesonide and ambroxol hydrochloride inhalation in children with pneumonia and their effects on inflammatory response
Abstract
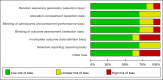
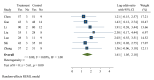
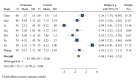
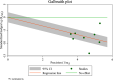
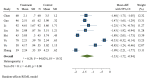
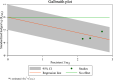
Childhood pneumonia, often caused by acute upper respiratory tract infections or bronchitis, is one of the leading causes of mortality in children. Nebulized inhalation, as a low-risk treatment method, has garnered significant attention. However, its effectiveness and safety remain controversial. In this study, a systematic review of relevant literature on the use of budesonide (BUD) and ambroxol hydrochloride (AMB) inhalation in the treatment of childhood pneumonia was conducted, and a total of 10 articles were included. The meta-analysis revealed an odds ratio (OR) of 1.61 and an I2 value of 0.00 % for the effectiveness of combined BUD and AMB inhalation therapy in children with pneumonia, indicating no heterogeneity among the studies in terms of effectiveness. The OR values for BUD or AMB inhalation in alleviating cough, lung auscultation abnormalities, respiratory distress, body temperature, and cyanosis of the lips in children with pneumonia all favored the combined BUD therapy, showing significant relief of the aforementioned symptoms. However, due to variations in drug dosage and administration methods, high heterogeneity was observed. This study suggested that combined BUD and AMB inhalation therapy has better efficacy in treating childhood pneumonia, and BUD combined with AMB inhalation is more effective in alleviating symptoms such as cough, lung auscultation abnormalities, respiratory distress, normalizing body temperature, and reducing cyanosis of the lips. Nevertheless, further validation is required due to the limited sample size and substantial heterogeneity in the included studies. To sum up, this study provides the first analysis of the efficacy and inflammatory response of BUD and AMB inhalation in children with pneumonia. Future research should aim to verify and clarify these findings, considering the limitations of the existing studies in terms of sample size and heterogeneity.
Keywords: Ambroxol hydrochloride; Budesonide; aerosol inhalation; meta-analysis; pneumonia.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures















Similar articles
-
The efficacy of nebulized budesonide and ambroxol hydrochloride in treating pediatric community-acquired pneumonia and their impact on clinical characteristics and inflammatory markers.J Health Popul Nutr. 2024 Aug 27;43(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s41043-024-00621-4. J Health Popul Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39192358 Free PMC article.
-
Aerosol inhalation of ambroxol hydrochloride combined with terbutaline can promote recovery of children with severe pneumonia.Am J Transl Res. 2021 May 15;13(5):5019-5026. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34150087 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical study of the oxygen drive aerosol inhalation with budesonide and ambroxol in the prevention of adult post-thoracotomy pneumonia].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Oct 18;50(5):840-844. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 30337745 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Budesonide inhalation suspension: a review of its use in infants, children and adults with inflammatory respiratory disorders.Drugs. 2000 Nov;60(5):1141-78. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200060050-00010. Drugs. 2000. PMID: 11129126 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of inhalation budesonide in the treatment of pediatric asthma in the emergency department: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pharmacol Rep. 2020 Aug;72(4):783-798. doi: 10.1007/s43440-020-00098-y. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Pharmacol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32227295
Cited by
-
Clinical study on modified Shenzhe Zhenqi Decoction combined with ambroxol hydrochloride in the treatment of severe pneumonia.Front Physiol. 2025 Jul 16;16:1601761. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1601761. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40740420 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy of azithromycin-budesonide combination therapy in pediatric Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Jul 15;17(7):5110-5119. doi: 10.62347/UFFC4110. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40821059 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of nebulized budesonide and ambroxol hydrochloride in treating pediatric community-acquired pneumonia and their impact on clinical characteristics and inflammatory markers.J Health Popul Nutr. 2024 Aug 27;43(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s41043-024-00621-4. J Health Popul Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39192358 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of inhaled ambroxol hydrochloride solution in patients with lower respiratory tract infectious diseases: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre clinical trial.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):830. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11194-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40596900 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Potential of Ambroxol as a Panacea for Neonatal Diseases: A Scoping Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 27;16(8):e67977. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67977. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39347262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yi Lili, Han Xiaohua, Liu Liyun, et al. Efficacy of atomized budesonide treating neonatal bronchopulmonary dysplasia after discharge from hospital[J] Int. J. Pediatr. 2018:456–459.
-
- Ghaiaty Ha El, Ismael Ym, Assar Eh, et al. Role of nebulized magnesium sulfate versus nebulized budesonide in treatment of acute bronchiolitis and its outcome[J] Benha Journal of Applied Sciences. 2021;6(6):267–273.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

